Topic Definitions #
Gate 1: Create a Vision?
the first phase of the project, often called the 'Idea' phase. It serves as an exciting starting point. To build a strong project model, the initiator, customer, or project manager must express a bold and ambitious vision for the future. This vision acts as a powerful foundation, inspiring the project's direction and potential.
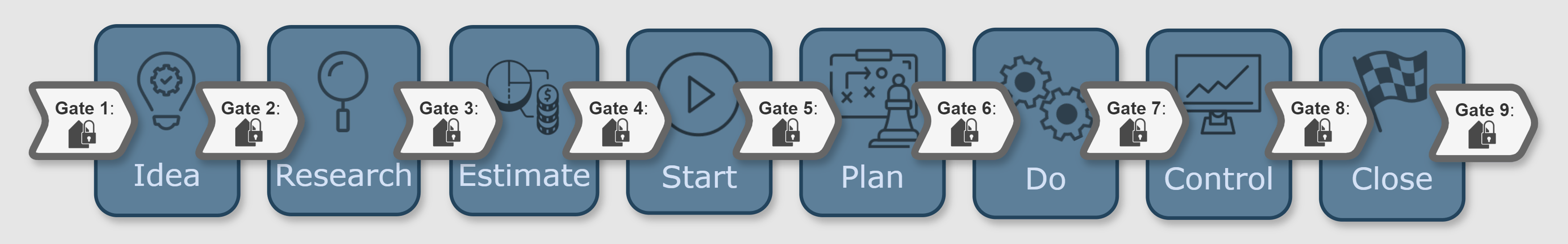
Project Phase Gates
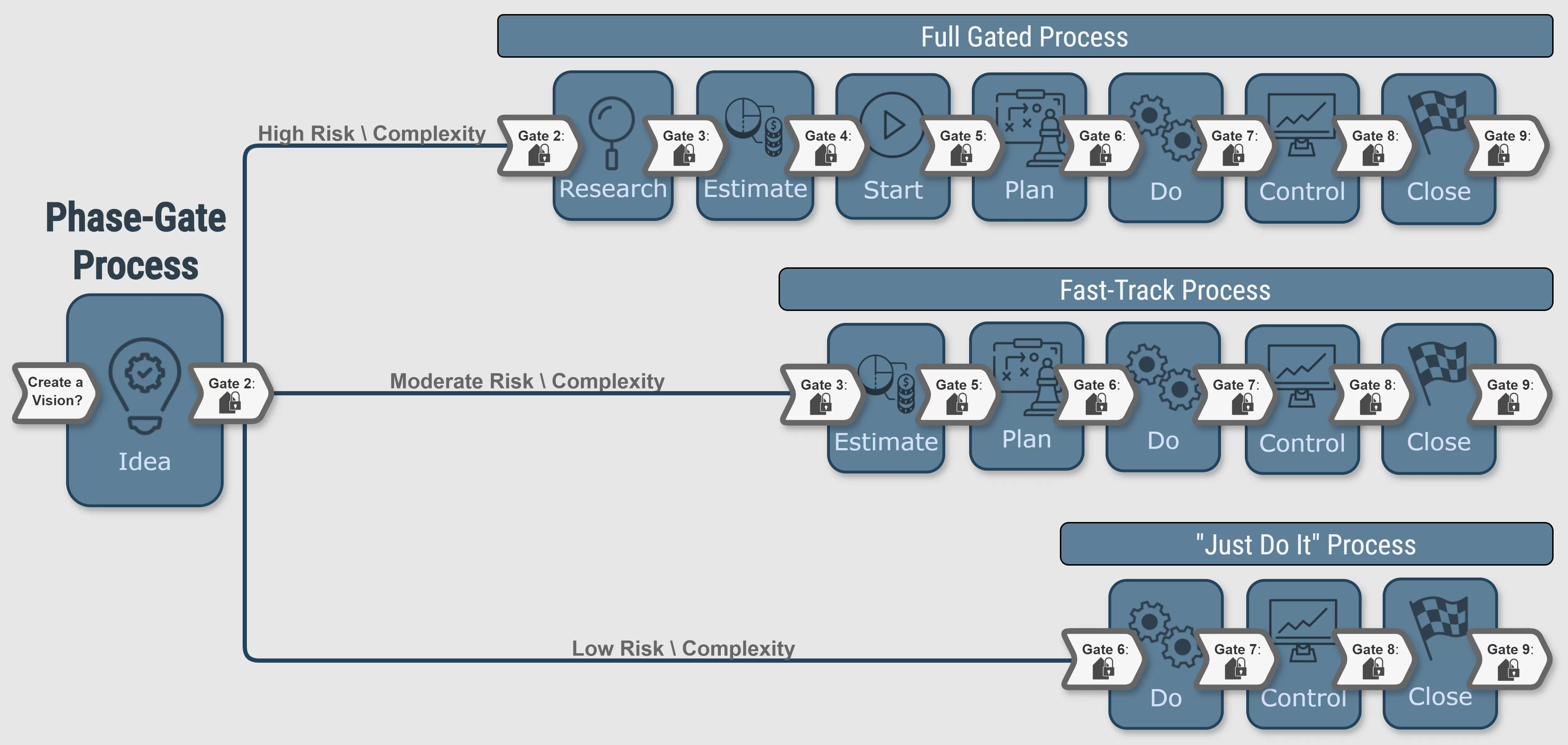
the continuation of the project is typically decided by a manager, steering committee, or governance board. This decision is thoughtfully made based on current forecasts and available information, which includes the risk analysis, and the availability of essential resources, such as funding and skilled personnel. In this way, the process ensures a well-informed path forward, aligned with project goals.
Phase-Gate Process
this is a highly effective project management technique in which an initiative or project—such as new product development, software creation, process improvement, or business transformation —is thoughtfully divided into distinct stages or phases. Each phase is separated by decision points, known as gates, so that progress can be carefully reviewed and aligned with the overall project goals.
Strategic Objectives
Tactical Plans
Operational Decisions
Alignment
Performance Indicators

Risk Identification

Socio-Cultural Factors
Demographics and Psychographics
Crafting a Compelling Project Vision #
Every successful project starts with an inspiring idea that directs all further development. That’s why defining a clear project vision is crucial. The vision not only initiates the project but also actively guides strategic decisions and daily team actions. Without a well-defined vision, teams may lose focus, causing even the most promising initiatives to drag on. However, with a strong vision, teams can stay on track and achieve their goals more efficiently.
We will explore how an idea transforms into the strategic foundation of a project and why organizations must establish a unified strategic management system. By analyzing different planning horizons—from long-term strategies to tactical operations—you will learn to effectively align business objectives with project tasks and strategies.
We will present various approaches and strategic management methods, using visual examples and diagrams to illustrate how an organization’s abstract ambitions connect with specific project goals and phases. Moving from theoretical definitions to practical tools like the “Mountain of Tomorrow” methodology, you will clearly understand how to develop and structure an initial project vision to ensure its successful implementation at every stage.
Demo Project Introduction: The Project We Will Build Throughout the Course
To move from abstract concepts to practical understanding, this course is built around a single demo project. Instead of isolated examples, we will consistently work with one business initiative and gradually develop it across all stages of project and business management.
The demo project represents a complex, real-world business scenario operating in a highly regulated, competitive, and technology-driven environment. It is intentionally designed to include strategic ambiguity, multiple stakeholder interests, and long-term growth ambitions.
In each article and learning module, we will expand this demo project step by step — from vision and strategy to goals, roadmaps, metrics, risks, and execution models. Every theoretical concept introduced in the course will be applied directly to this project.
By the end of the course, learners will not only understand business and project management concepts but will also have a complete, structured project framework that can be adapted to their own real initiatives.
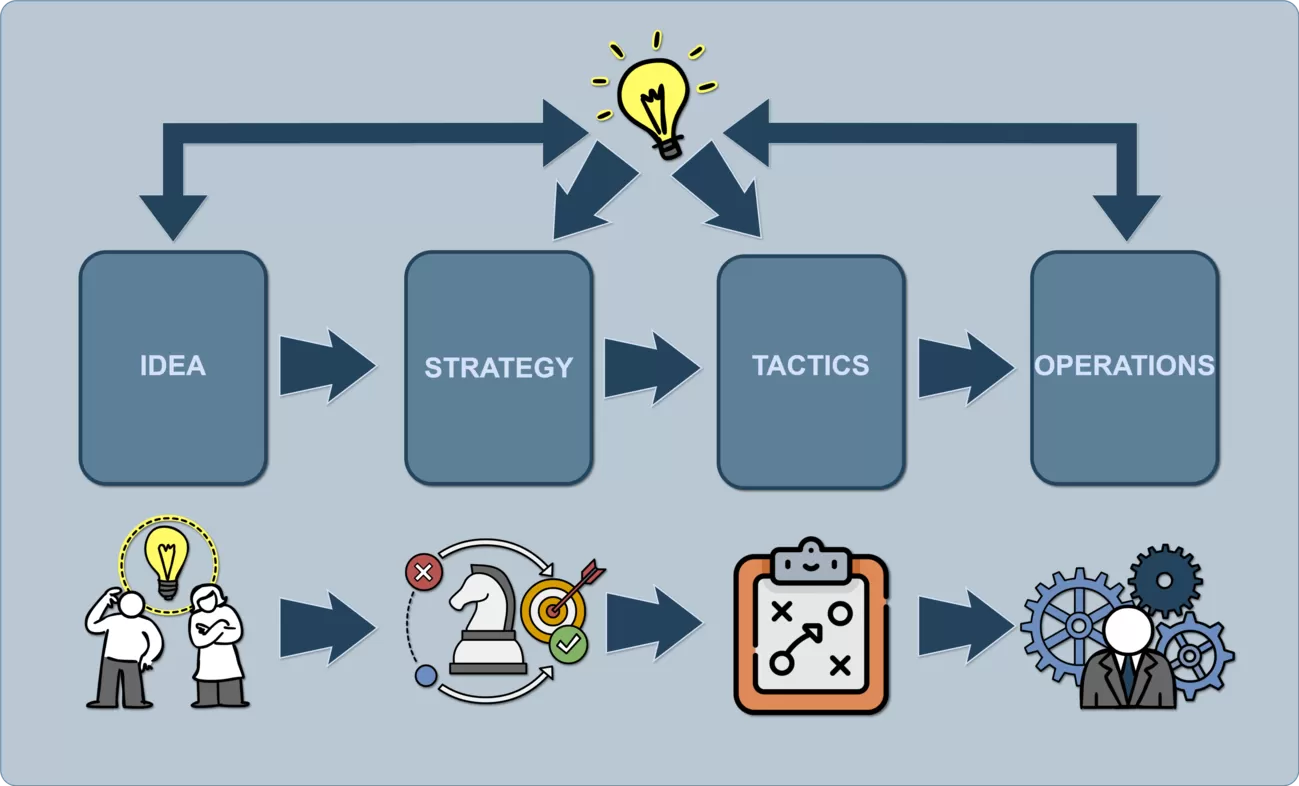
Horizons of Strategy and Planning #
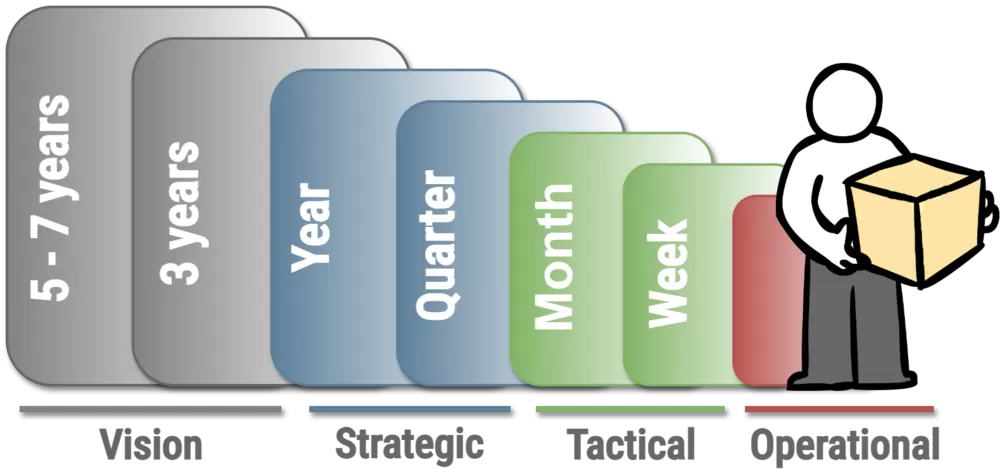
Strategic planning happens across different time horizons. Long-term visions span 5–7 years, while strategic objectives focus on annual or quarterly goals. Tactical plans cover monthly and weekly targets, whereas operational decisions ensure daily execution. Understanding these levels helps align project goals with broader business strategies.
To Create a Vision, it is Necessary to Create a Strategic Management System for an Organization or Business #
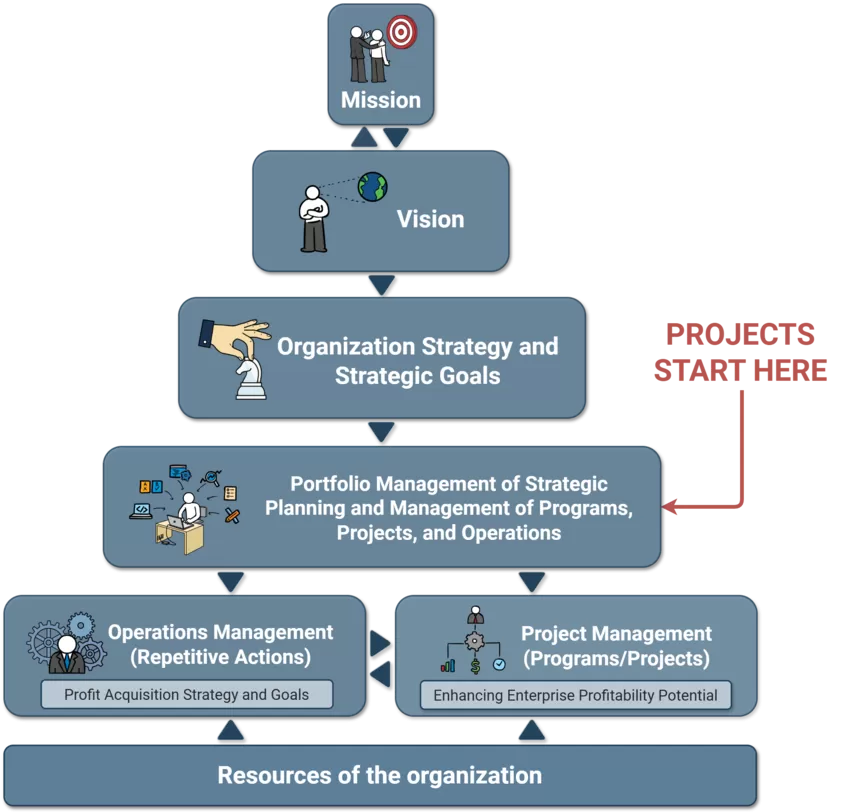
For an organization or business to create a strong vision, it must develop a strategic management system. The process begins with defining a mission—the core reason for its existence. Next, it establishes a vision, outlining its long-term aspirations. These elements guide the organization’s strategy, ensuring all projects align with strategic goals.
Projects originate within this structured framework. By integrating them into a broader strategy, businesses ensure that every initiative contributes to long-term success.
Strategic Context
To move from abstract concepts to practical understanding, this course is built around a single demo project. Instead of isolated examples, we will consistently work with one business initiative and gradually develop it across all stages of project and business management.
The demo project represents a complex, real-world business scenario operating in a highly regulated, competitive, and technology-driven environment. It is intentionally designed to include strategic ambiguity, multiple stakeholder interests, and long-term growth ambitions.
In each article and learning module, we will expand this demo project step by step — from vision and strategy to goals, roadmaps, metrics, risks, and execution models. Every theoretical concept introduced in the course will be applied directly to this project.
Strategic Modalities #
Mission
Explains why the project / business exists. It provides a clear direction for decision-making and reflects current realities. Unlike short-term strategies, a mission follows a long-term visionary approach without strict time limitations, making it valuable for both internal and external communication.
Vision
Fixes an idea of the future of the project / business. It serves as a roadmap for shaping strategy and responding to evolving circumstances. Designed with specific timeframes, it primarily supports internal objectives. However, strong vision statements also resonate effectively with external audiences.
Strategy
A strategy turns vision into reality. It consists of a carefully structured plan that exceeds costs while delivering maximum value. Strategies require continuous refinement, customer insights, and industry changes. Unlike a vision, which provides direction, a strategy focuses on execution.
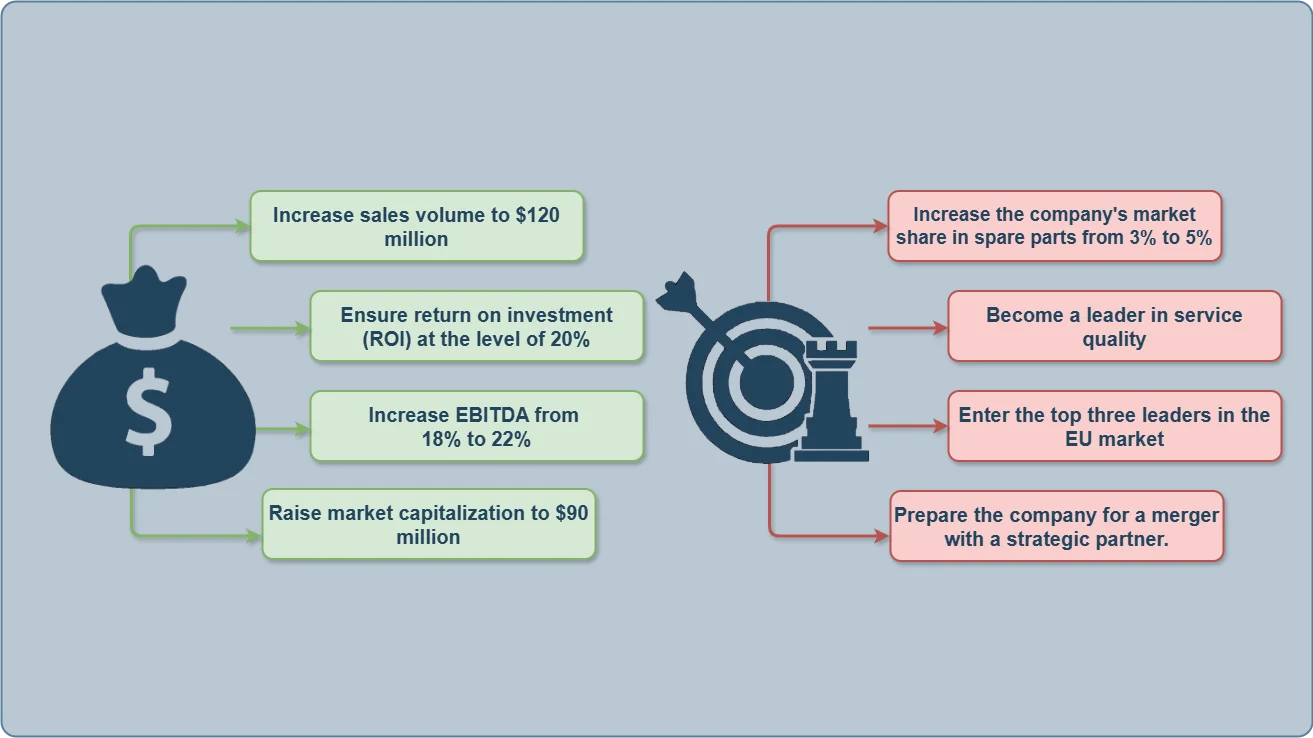
Business Goals and Strategies
- Business goals and strategies define an organization's overall direction, forming the foundation for growth.
- Business goals represent the organization's ultimate ambitions.
Strategies serve as structured pathways that guide the organization toward achieving these goals.
Each project contributes to this broader framework by aligning with organizational objectives and strategies.

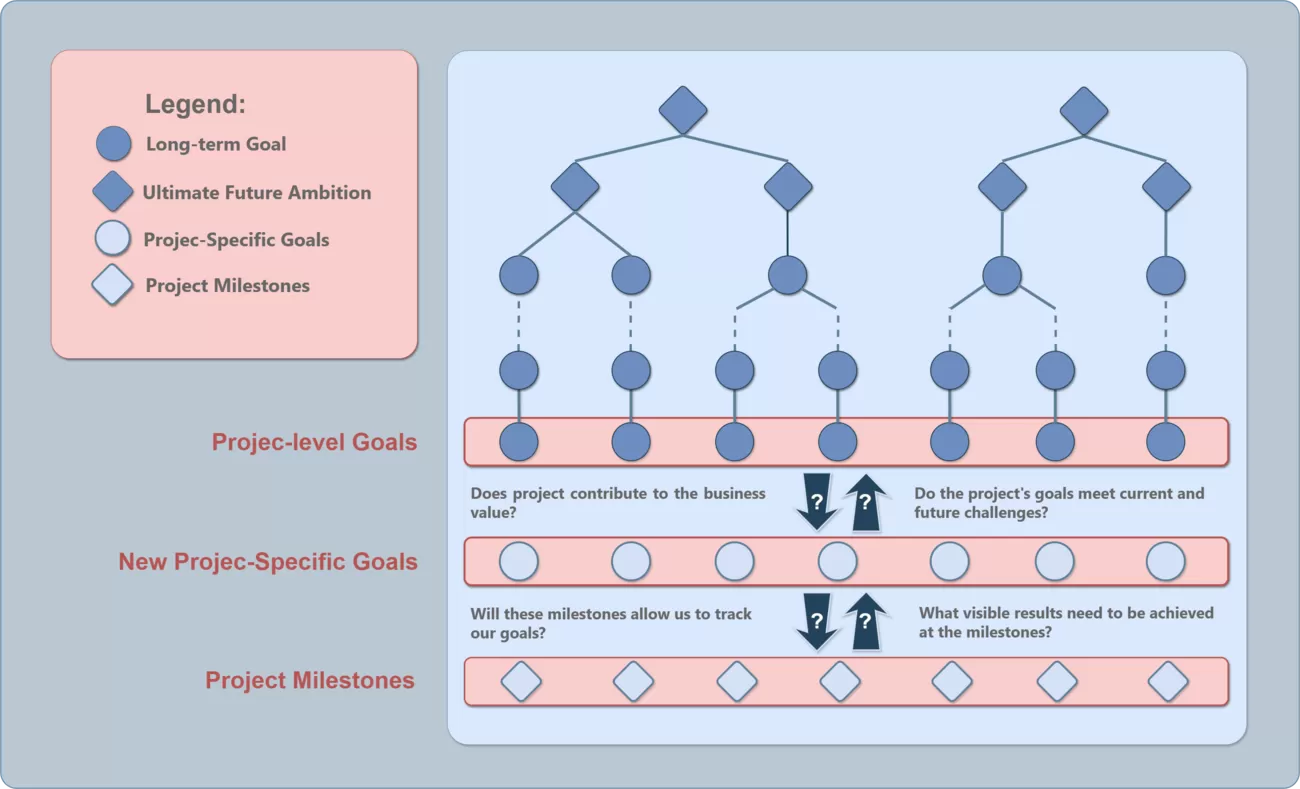
Project-level Goals (Goal Catalog)
New Project-specific Goals
- At the bottom level , there are new goals specific to each project. These goals are positively focused on achieving concrete results and completing tasks within a specific project. Their purpose is to actively support the achievement of project-level goals, which, in turn, help drive the organization’s goals and strategies.These goals also foster innovation and continuous improvement, ensuring that each project delivers measurable value to the organization.
Project Milestones
How Project Milestones are Formed #
1.From Project-specific Goals:
- Once the project-specific goals are clearly established, these goals are thoughtfully broken down into actionable tasks and phases. Each task is then mapped to specific milestones, which mark important points where key deliverables and positive results can be achieved. This process ensures that the project moves forward in an organized and measurable way.

2.Tracking Progress:
Regular milestone reviews help identify potential risk early, allowing teams to proactively address challenges before they escalate.
3.Alignment with Organizational Objectives:
4.Examples of key milestones include:
Today's Challenges #
Today’s Challenges are obstacles during project launch, planning, and scope definition, including market conditions, technical tasks, and stakeholder support. Addressing them is key to project success.
Market Challenge
involves competition, shortages of supply, changes in consumer behaviour, demographics and psychographics, socio-cultural factors.
Project Challenge
involves the solution to be designed, developed and delivered to solve a problem or address an opportunity within a given project.
Adopt Challenge
It involves the importance of the human aspect of change, considers their need for support, and ensures a positive impact on all participants
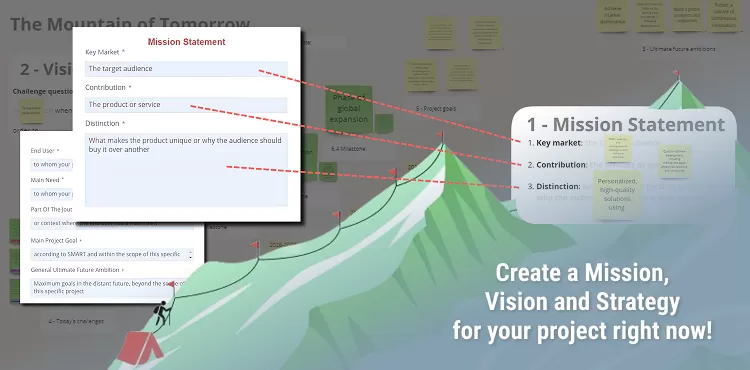
The Mountain of Tomorrow - Brainstorming of the Mission, Vision and Strategy of the Project #
The ‘Mountain of Tomorrow’ framework helps teams develop a clear mission, vision, and strategy. By visualizing key objectives and challenges, teams can create actionable plans that drive long-term success and help them Create a Vision rooted in purpose and measurable impact.
Demo Project Overview
Throughout this course, this demo project will evolve alongside your learning journey. Step by step, you will build a complete project structure — from vision and strategic alignment to goals, milestones, metrics, and execution models.
By the end of the course, you will be able to replicate this approach for your own business ideas, startups, or corporate initiatives.

![]() Primary Market:
Primary Market:
United States
![]() Target Customers:
Target Customers:
Retail customers and small business segments, including startups, freelancers, e-commerce operators, and digital product creators.
![]() Project Scope (High-Level):
Project Scope (High-Level):
The project focuses on launching a mobile-first banking platform that provides everyday financial services, including account management, payments, and digital financial tools. The platform is designed to operate in a highly regulated environment and to meet both individual and small business needs.
![]() Strategic Ambition:
Strategic Ambition:
Although the initial launch targets the U.S. market, the project is architected with a global-first mindset. The long-term ambition is to enable international expansion through modular compliance, scalable infrastructure, and open APIs.
![]() Key Characteristics:
Key Characteristics:
- mobile-first and fully digital onboarding
- strong regulatory and compliance requirements
- high competition in the neobank and fintech space
- emphasis on transparency, usability, and service reliability
- long-term platform and ecosystem orientation
![]() Role in the Course:
Role in the Course:
This project serves as the central demo case for the entire learning cycle. All strategic, managerial, and project-related concepts introduced in the course are applied to this project step by step, allowing learners to observe how a complex business initiative is developed from vision to execution.
Conclusion #
A well-crafted project vision is far more than a motivational statement—it is the strategic compass that guides every phase of development, from concept to execution. By anchoring the project in a structured strategic management system that connects mission, vision, and strategy, organizations ensure that their initiatives are purpose-driven and aligned with long-term goals.
Understanding the horizons of planning — from long-term ambitions to daily operations—enables teams to synchronize business and project-level goals. Through frameworks like the “Mountain of Tomorrow,” teams can Create a Vision that transforms abstract aspirations into actionable milestones that are both measurable and strategically relevant. Each milestone then becomes a marker of progress, ensuring consistent alignment with broader organizational objectives.
In an environment shaped by market pressures, project complexity, and the need for human-centered change, a strong vision provides stability, focus, and direction. It empowers teams to Create a Vision that responds effectively to today’s challenges, fosters innovation, and ultimately delivers outcomes that drive sustainable success.