Topic Definitions #
RACI Matrix #
PESTEL Analysis #
JTBD #
PII #
SWOT #

PEST #
Strategy Synthesis #
SWOT Analysis #
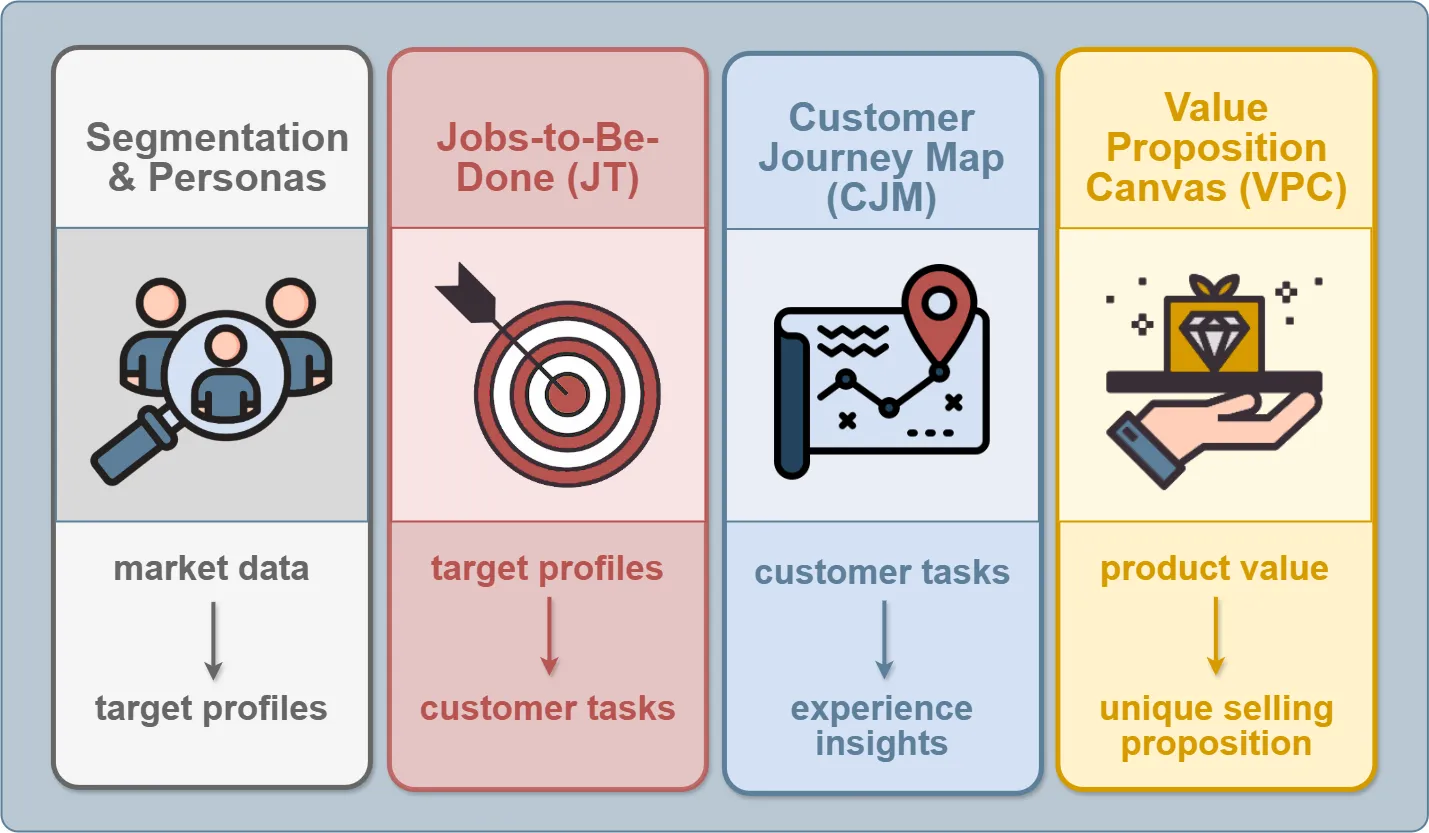
From Segmentation to USP: The Logic of Building a Value Proposition #

Purpose: #
- This step shifts the focus of analysis from the external environment to the internal market and the customer.
If macro factors (PESTEL, scenarios, sensitivity analysis) have shown the environment in which the project will exist, now we define who it will exist for and why they will choose it.
Key tasks: #
- Translate SWOT hypotheses into strategic decisions.
- Formulate goals, positioning, and growth approaches.
- Build a system for measuring and managing growth.
This block creates the substantive foundation for further identification of SWOT internal forces — S/W (Strengths & Weaknesses) — by building Critical Success Factors and conducting comparative analysis with competitors.
Overall Logic (Input → Output) #
| Input from the previous article | Tool of the current step | Output to the next article |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental scenarios (S1–S3), macro trends, project sensitivity | Segmentation & Personas, JTBD, CJM, VPC → USP | Foundation for Competitive Analysis & OSINT (SWOT S/W) |
This is how we move from PESTEL/Scenario data to customers’ behavioral and emotional insights, which then become the basis for positioning and competitive strategy.
Analysis Structure (Infographic For The Introductory Block) #
1. Customer Insight Stack
- JTBD: translates customer personas into specific tasks and desired outcomes.
- CJM: shows exactly where barriers and emotions arise along the journey.
- VPC → USP: turns insights into a clear value proposition and a unique selling proposition.
- Next: we carry this value into competitive analysis to validate uniqueness and shape positioning.
1. Segmentation & Personas #

Purpose: #
- Identify customer groups that differ in behavior, values, and expectations of the product. At this stage, we transform the results of the macro-level environment analysis into concrete portraits of target users, creating the “human layer” of the research.
- JTBD: translates customer personas into specific tasks and desired outcomes.
- CJM: shows exactly where barriers and emotions arise along the journey.
- VPC → USP: turns insights into a clear value proposition and a unique selling proposition.
- Next: we carry this value into competitive analysis to validate uniqueness and shape positioning.
Transition Logic (Input → Output) #
| Input (From Macro Factors Analysis) | Tool Used | Output (For JTBD) |
|---|---|---|
| Macro trends, socio-economic and technological factors, industry development scenarios | Segmentation (Demographic, Behavioral, Psychographic) | Personas with clearly defined motivations, pain points, and digital habits |
Key Macro Factors Influencing Segmentation #
| Factor Group | Key Takeaways | Impact On Segmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Social | Growing share of Millennials and Gen Z in the workforce; strong preference for digital mobility and an ESG agenda | Formation of the Digital-First Millennials segment |
| Technological | Wider adoption of FinTech, open APIs, crypto payments, and remote identification (e-KYC) | Supports segments with higher trust in online platforms |
| Economic | Increasing role of small businesses, freelancers, and startups; need for flexible banking tools | Formation of the SME Owners & Freelancers segment |
| Cultural | Rising popularity of ethically oriented investing and preference for sustainable brands | Formation of the ESG Investors segment |
| Regulatory | Simplification of KYC and financial institution accreditation procedures; incentives for innovation | Enables focus on “legal fintech” and remote account opening |
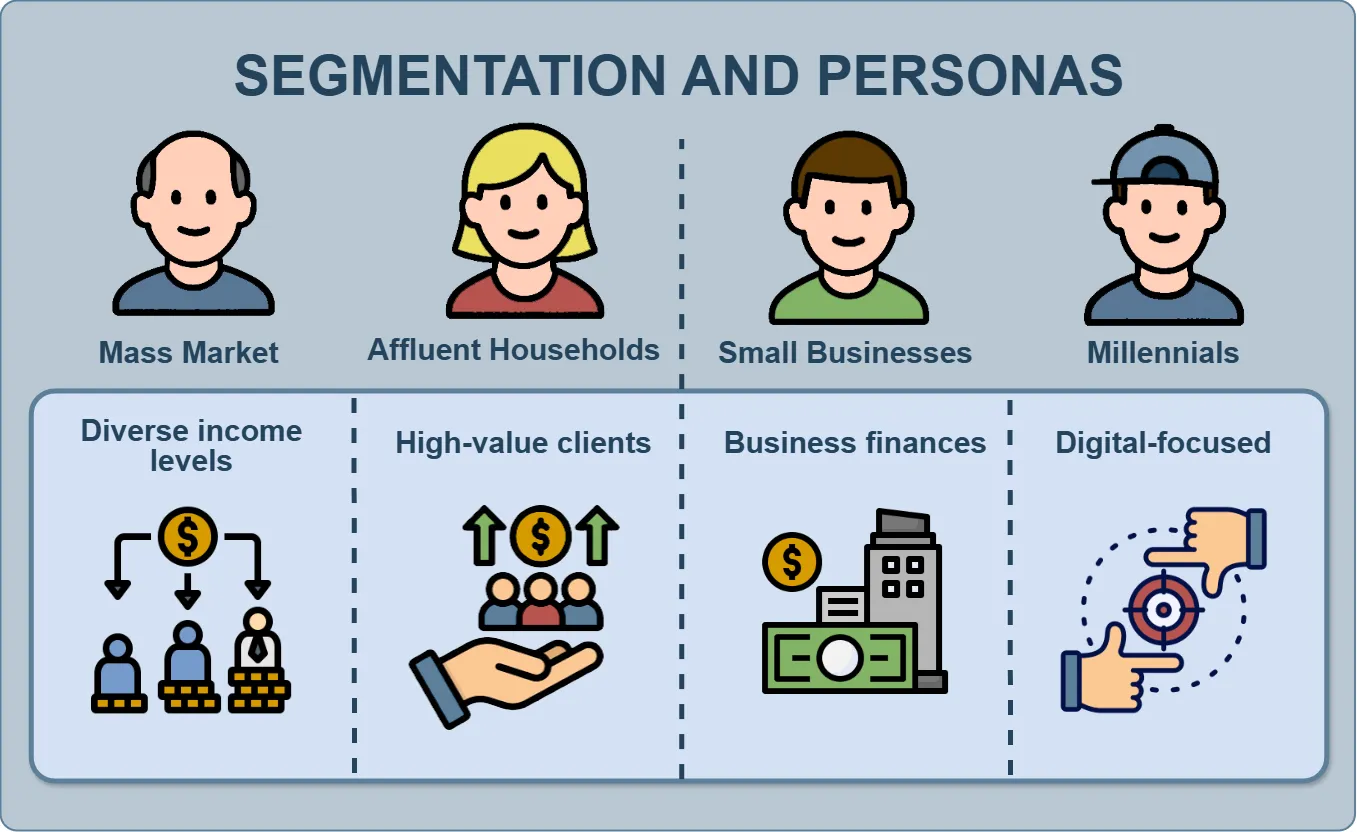
Segmentation #
Based on these factors, three key customer segments were identified—each representing different expectations of the new bank being launched in the U.S.
| # | Segment | Key Motivation | Behavior | Primary Interaction Channels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | ESG Investors | Ethical investing, sustainability, transparency | Long-term portfolios, avoidance of “dirty” industries | ESG investing platforms, analytics portals |
| 3 | SME Owners & Freelancers | Simplicity, speed, and minimal bureaucracy | Use online banking and financial automation | Web portals, CRM plugins, API integrations |
| 1 | Digital-First Millennials | Convenience and control through digital solutions | Fully online: mobile wallets, P2P, crypto payments | Mobile apps, social media, referral programs |
Persona Development #
For each segment, persona cards are created based on demographic, behavioral, and psychographic data. A persona card is a tool that translates numbers into human language while preserving the context of the customer’s pain points and expectations.
| Persona | Description | Key Pain Points | Values & Expectations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emma, 29 — Digital-First Millennial | Lives in San Francisco, does everything via phone, invests small amounts in crypto and ETFs | Slow interbank transfers, hidden fees, outdated UX | Simplicity, instant transfers, transparent pricing |
| Linda, 44 — SME Owner | Runs an online store, hires freelancers, makes many payments | Bureaucracy, slow support, no CRM integration | Simple operations, APIs for automation, 24/7 support |
| Robert, 38 — ESG Investor | Financial analyst, invests in sustainable companies, reads ESG reports | Lack of trust in banks without transparency; no verification tools | Ethical focus, access to ESG ratings, transparent portfolio structure |
Persona Portfolio Dashboard #
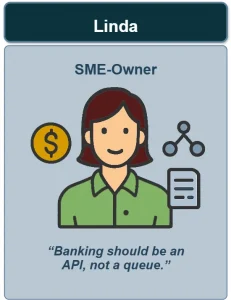


Illustration Structure:
- Three cards with avatars of the personas.
- Under each avatar: a short quote reflecting their attitude toward the bank.
- Small icons indicate behavior: communication, finance, digitalization.
- Captions show the transition “Insight → JTBD,” for example:
- Emma: “I want my bank to feel like my phone — fast and intuitive.”
- Robert: “If I don’t see how you invest, I don’t invest with you.”
- Linda: “Banking should be an API, not a queue.”
Linkage To Subsequent Tools #
| Current Tool | Output | Input for The Next Step |
|---|---|---|
| Segmentation & Personas | Deep understanding of customers and their context | Jobs-to-Be-Done (defining functional and emotional jobs) |
2. Jobs-to-Be-Done (JTBD) #

Purpose: #
- Identify which real tasks (jobs) the customer is trying to accomplish when interacting with the product—functional, emotional, and related/social—and what results (desired outcomes) they expect to achieve.
The JTBD Canvas helps you capture not just what the user does, but why they do it and what matters to them in the end.
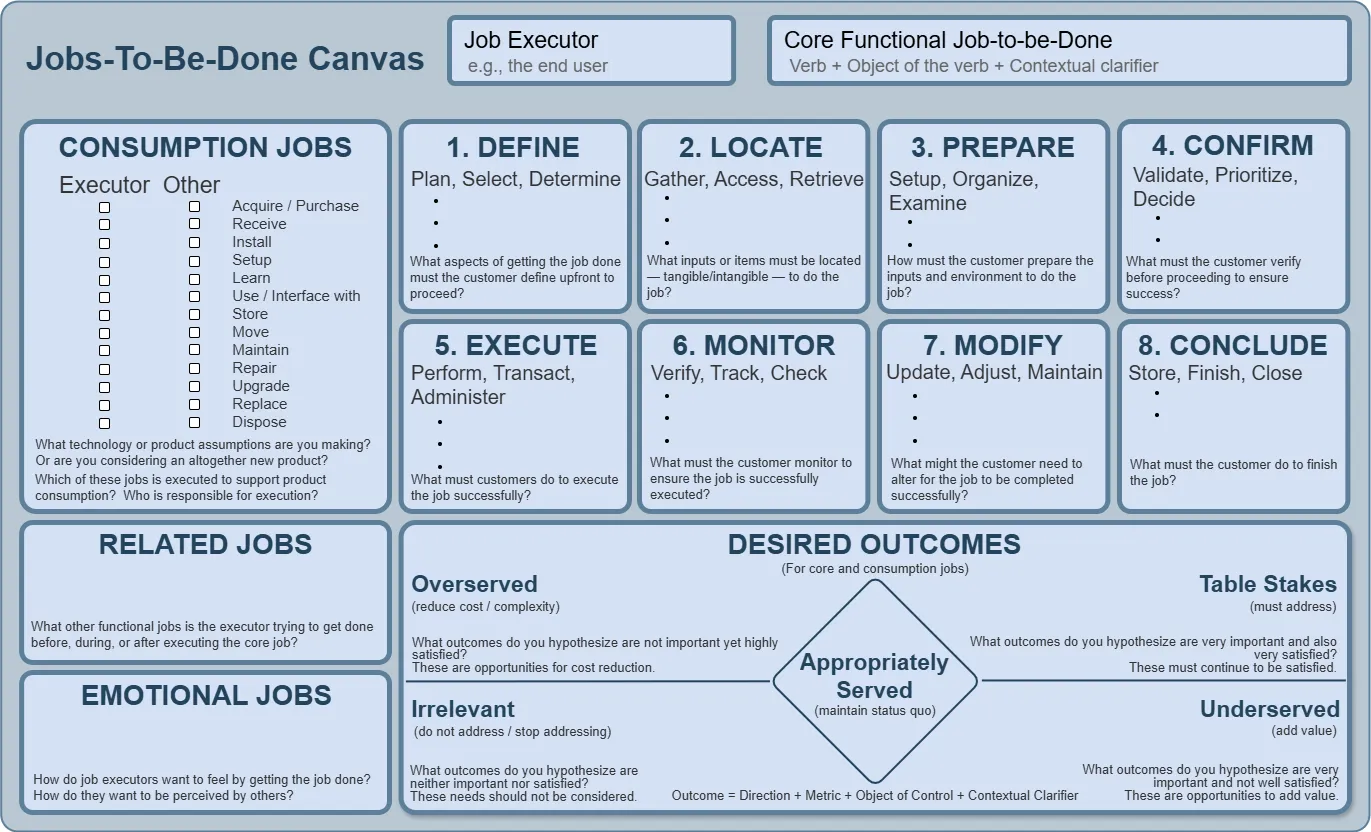
Jobs-to-Be-Done Canvas Template #
The template is divided into several functional blocks:

1. Job Executor #
-
Who performs the job.
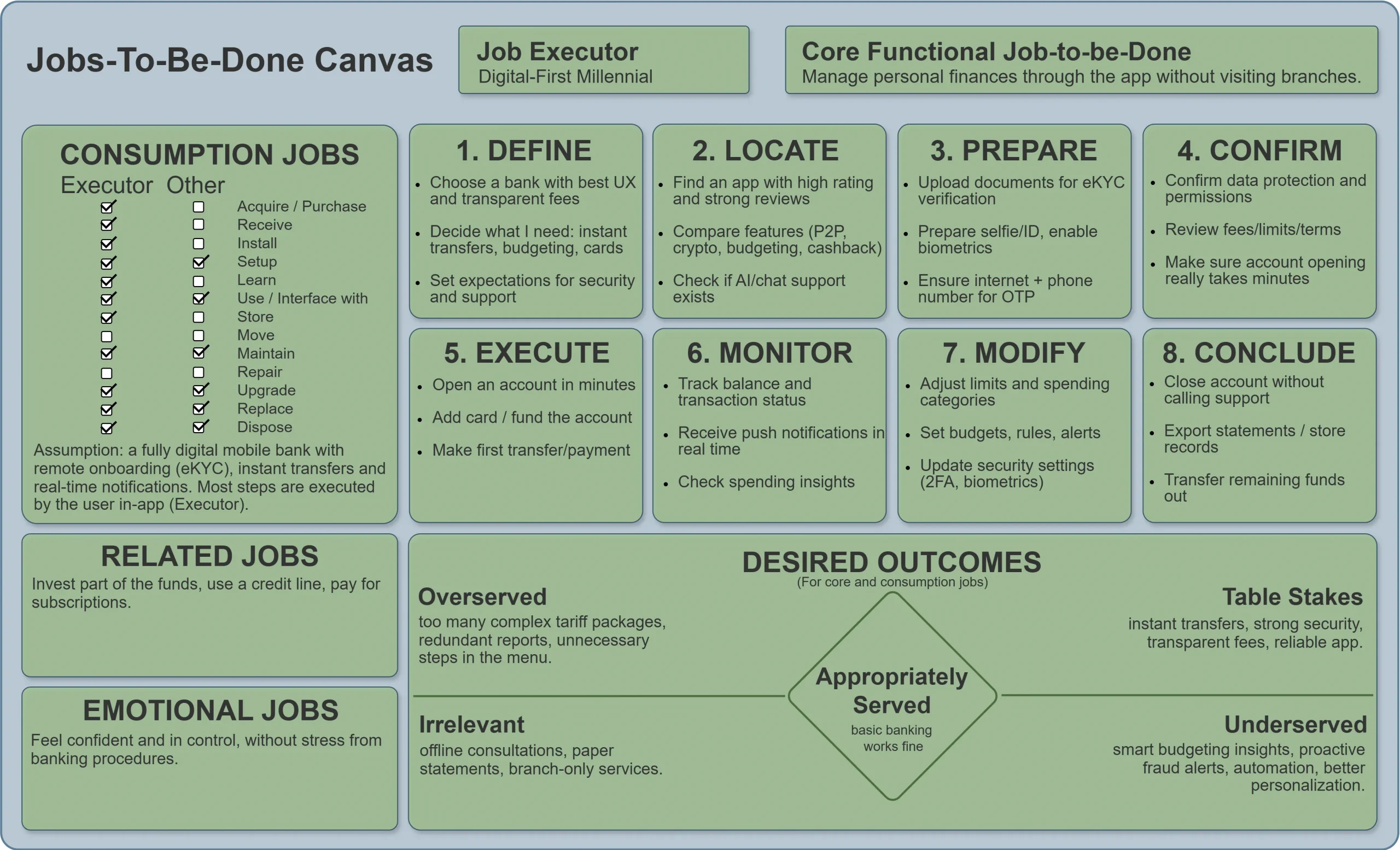
- In our case: a Digital-First Millennial — a young customer who uses only digital banking services.

2. Core Functional Job-to-be-Done #
-
The main “job” the customer hires the product to do.
- Formula: verb + object + context.
- For example: “Manage personal finances quickly and without bureaucracy in a mobile bank.”

3. Consumption Jobs #
- Supporting tasks that accompany the customer’s core job. They describe the lifecycle of interaction—from choosing to using and updating the product.
An 8-step structure:
| № | Stage | Examples for a U.S. banking case |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define | Determine which bank matches my expectations for speed and transparency |
| 2 | Locate | Find an online bank with a simple account-opening process |
| 3 | Prepare | Prepare documents for online verification |
| 4 | Confirm | Review the terms, fees, and the bank’s reputation |
| 5 | Execute | Open an account in the app and transfer funds |
| 6 | Monitor | Track balance and notifications in real time |
| 7 | Modify | Adjust limits, notifications, and the interface |
| 8 | Conclude | Complete transactions, close the account, or transfer assets |
4. Related Jobs #
-
Tasks the customer performs in parallel with, or after, the core job.
- Example: tracking a credit score, managing a personal budget, managing investments.

5. Emotional Jobs #
-
Reflect the feelings the customer wants to experience while completing the job, and how they want to be perceived by others.
- Internal emotions: “I’m in control of my finances—not the other way around.”
- Social emotions: “I use a modern, well-designed bank—like my fintech friends do.”

6. Desired Outcomes #
-
The results the customer wants to achieve and their priority.
- Table Stakes — mandatory expectations (must-have).
- Opportunities to Add Value — expectations where you can outperform competitors.
The Canvas suggests looking at them across two dimensions:
Example of filling out the Jobs-to-Be-Done Canvas #
(persona: Digital-First Millennial, product: U.S. mobile bank)
3. Customer Journey Map (CJM) #

Purpose: #
- A Customer Journey Map (CJM) is a tool that visualizes the customer’s path from initial awareness to building loyalty. It helps identify where the customer faces difficulties, what triggers positive emotions, and how the company can improve interactions at each stage.
- A CJM brings together insights from Jobs-to-Be-Done and Personas, turning behavioral insights into a manageable customer experience strategy.
What a Customer Journey Map is #
A CJM is a visual map of the customer journey that includes:
Interaction stages (stages);
The customer’s actions, thoughts, and emotions;
Touchpoints—digital and physical;
Pain points and opportunities for improvement.

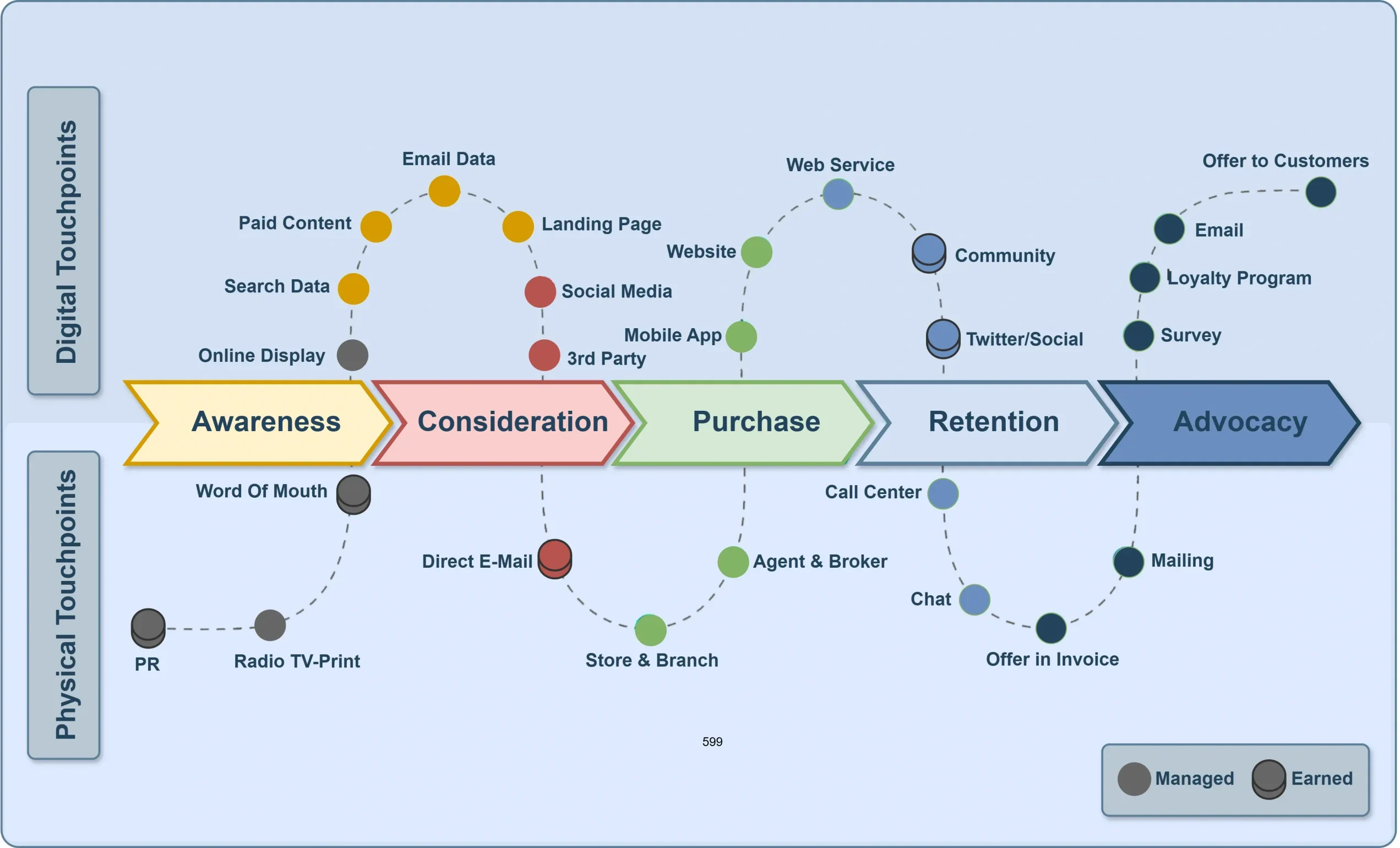
What it Shows: #
- The customer flow from Awareness to Advocacy.
- Vertical axes for “emotions” and “experience.”
- Small icons for touchpoints and pain points.
- Add labels: What client does / thinks / feels / experiences.
- At the bottom, add a note: “CJM = behavior + emotions + interactions.”
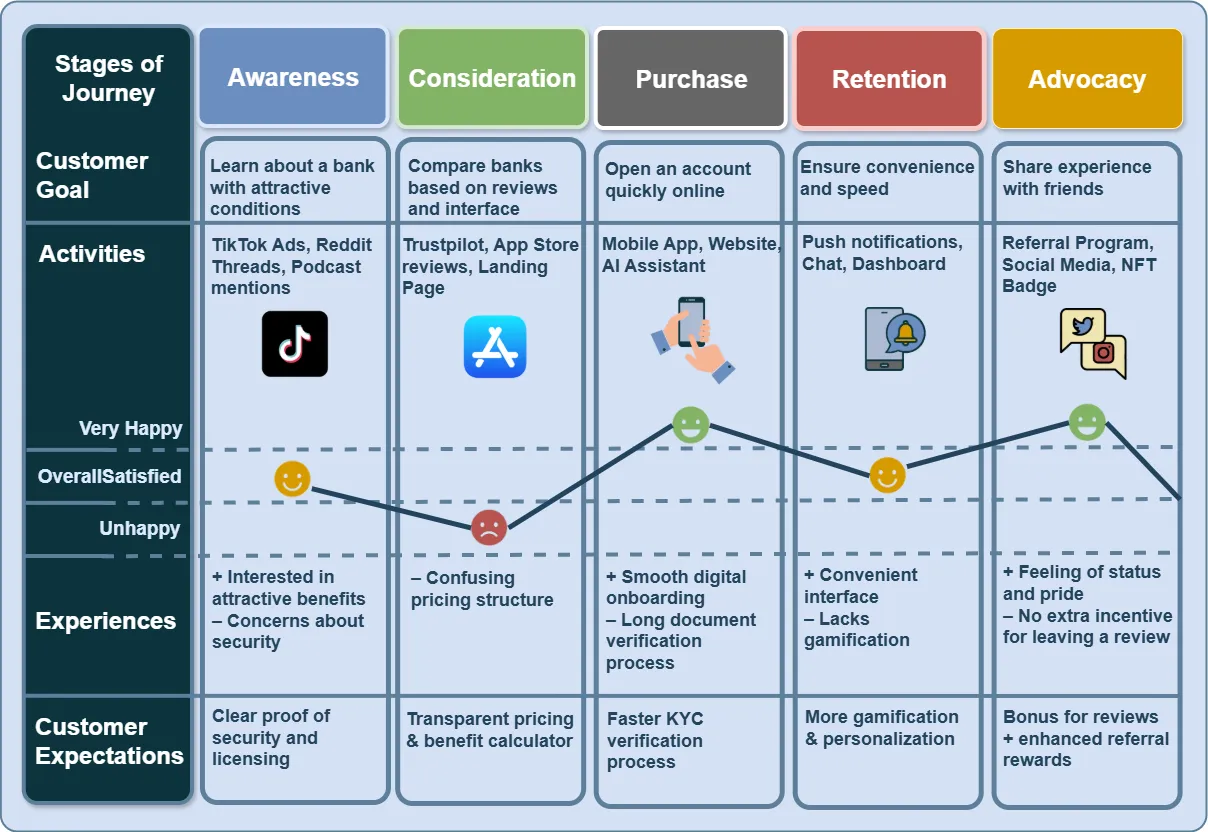
Stages of the Customer Journey #
The Customer Journey is divided into five key stages, each with its own goals, content, and channels:
| Stage | Customer Goal | Key Actions | Success Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchase | Make a decision and complete the purchase | Visits the website, talks to a consultant | Conversion rate |
| Retention | Evaluate the experience and stay | Receives notifications, uses the service | LTV, repeat actions |
| Advocacy | Share the experience | Shares a review, recommends | NPS, UGC |
| Awareness | Learn about the brand or product | Reads, listens, sees ads | Awareness level |
| Consideration | Compare options | Reads reviews, evaluates benefits | Engagement, CTR |

What it Shows: #
- The customer flow from Awareness to Advocacy.
- Vertical axes for “emotions” and “experience.”
- Small icons for touchpoints and pain points.
- Add labels: What client does / thinks / feels / experiences.
- At the bottom, add a note: “CJM = behavior + emotions + interactions.”

Touchpoints: #
- Touchpoints are the key elements of a customer journey map that help you visualize how people interact with your brand across different stages of their experience. The exact number of touchpoints can vary significantly depending on the product, industry, and customer behavior, which is why identifying them is always a highly individual process.
To define touchpoints effectively, it is important to carefully analyze a typical customer journey and document each step along the way. Once identified, all interaction points should be arranged sequentially to provide a clear and complete picture of the overall customer experience.
Digital Touchpoints: #
- Digital touchpoints form the foundation of a modern Customer Journey Map (CJM). They enable seamless, instant, and personalized interactions that meet the expectations of today’s customers. Digital channels play a particularly important role during the awareness, consideration, and retention stages, where customers expect fast access to information and convenient ways to engage with the brand.
Add relevant modern touchpoints: #
-
Social & Media: #
TikTok Ads, YouTube Shorts, Influencer Reels, Reddit threads.
-
Owned Channels: #
Website, App Store page, Mobile app, AI chat assistant, Push notifications.
-
Engagement & Retention: #
Email automation, Loyalty programs, Referral bots, Gamified dashboards.
-

Emerging Channels: #
Web3 wallet integration, AI-powered credit assistant, Telegram/Discord finance communities.
Add relevant modern touchpoints: #
- Awareness → short-form videos, paid media
- Consideration → social proof, user reviews
- Purchase → onboarding flow, identity verification
- Retention → app dashboard, chatbot support
- Advocacy → user-generated content (UGC), referral tokens

Physical Touchpoints: #
- Despite increasing digitalization, physical touchpoints remain critical for building trust.
In the banking sector, tangible interactions are especially important, as they create a sense of reliability and personal connection.
Modern physical touchpoints include: #
-

Events & PR: #
financial seminars, PR conferences, collaborations with lifestyle venues.
-

Experience Zones: #
pop-up spaces in shopping malls, VR demos, co-working banking points.
-

Customer Service: #
agent locations, call centers, face-to-face consultations.
-

Community: #
partner events, charity initiatives, sports sponsorships.
Synchronization with digital channels is achieved through QR activations, eKYC verification, and CRM integration.
Example of a Completed Customer Journey Map #
Case: Opening a bank account in the U.S.
A blended customer journey that combines digital-first channels with a physical presence.
Persona: Emma, 29 — a digital-first millennial
Online Shopping Customer Journey Map
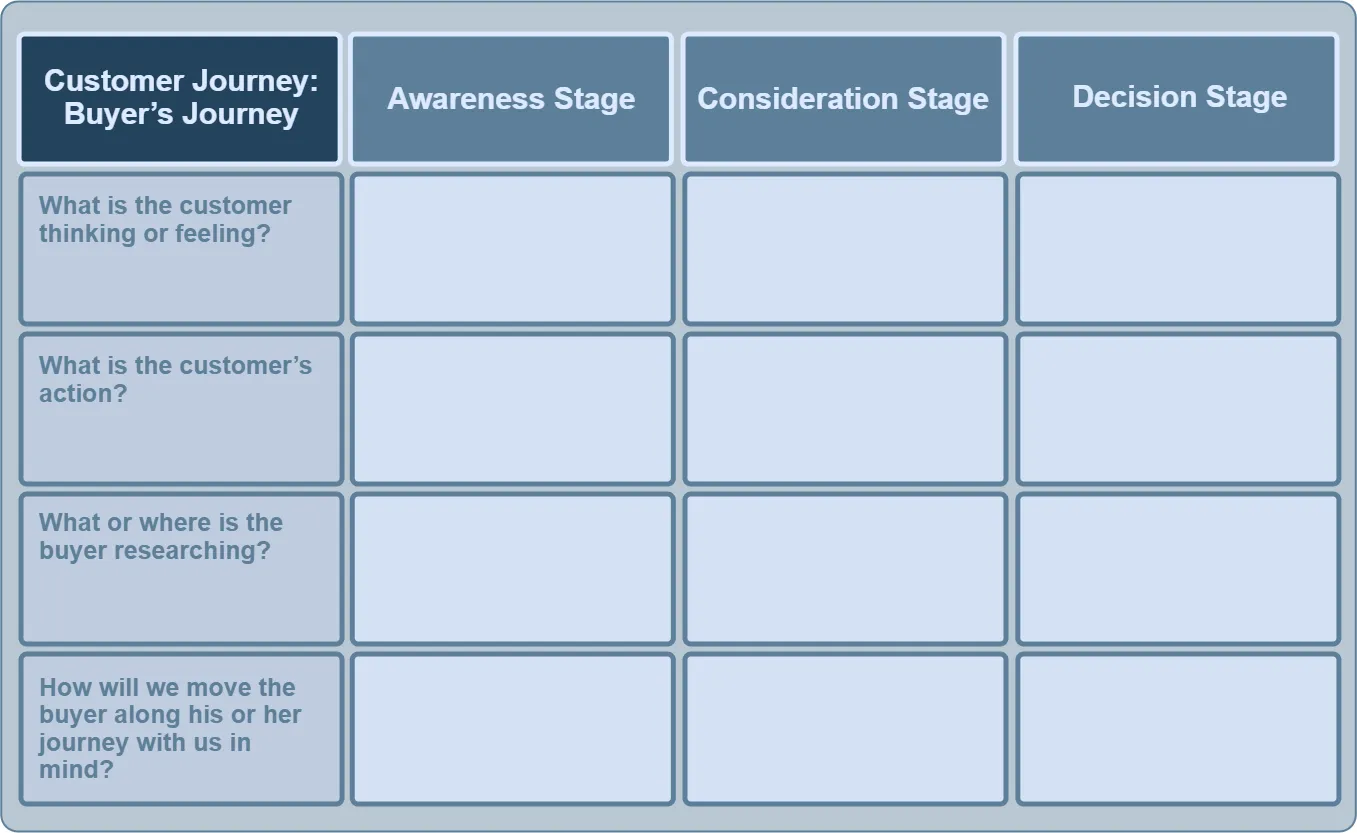
CJM Blank Template #
As we have just mentioned, this is a widely recognized type of customer journey mapping.
When creating a customer journey map, you track the key stages of the customer journey (awareness, consideration, purchase, and so on), as described above, along with the customer touchpoints associated with each stage.
A blank template for independently completing the Customer Journey Map (CJM) for each segment:
Thinking / Feeling
Action
Research
Brand Guidance
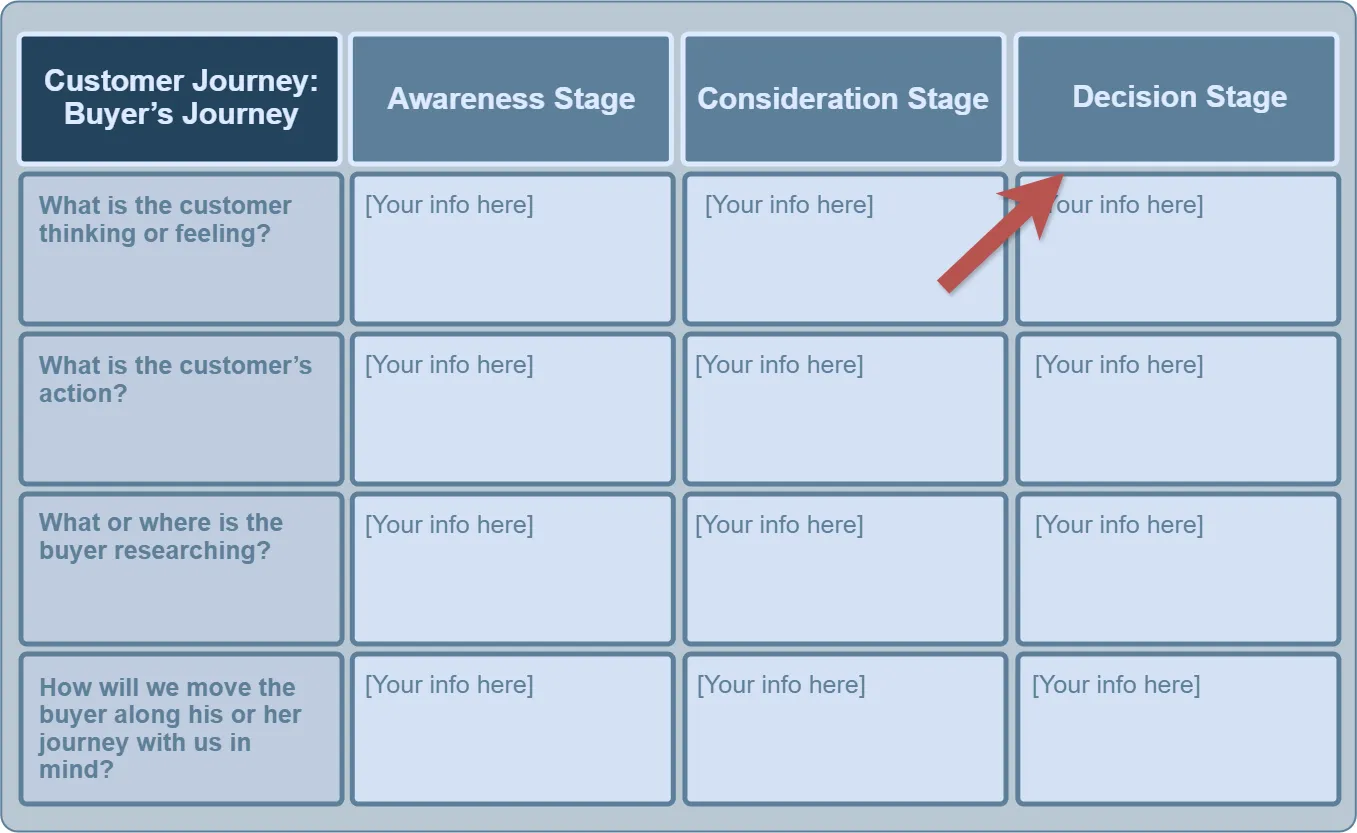
Customizable Template #
The default starting point is intentionally simple. It includes only three stages and a small set of questions designed to help understand customer interactions. However, you can easily add more stages, questions, and additional information to fully customize the buyer’s journey based on the specific needs and characteristics of your business.
Demonstrate the ability to add additional stages:
- Onboarding Experience
- Abandonment Recovery
- Upgrade Decision
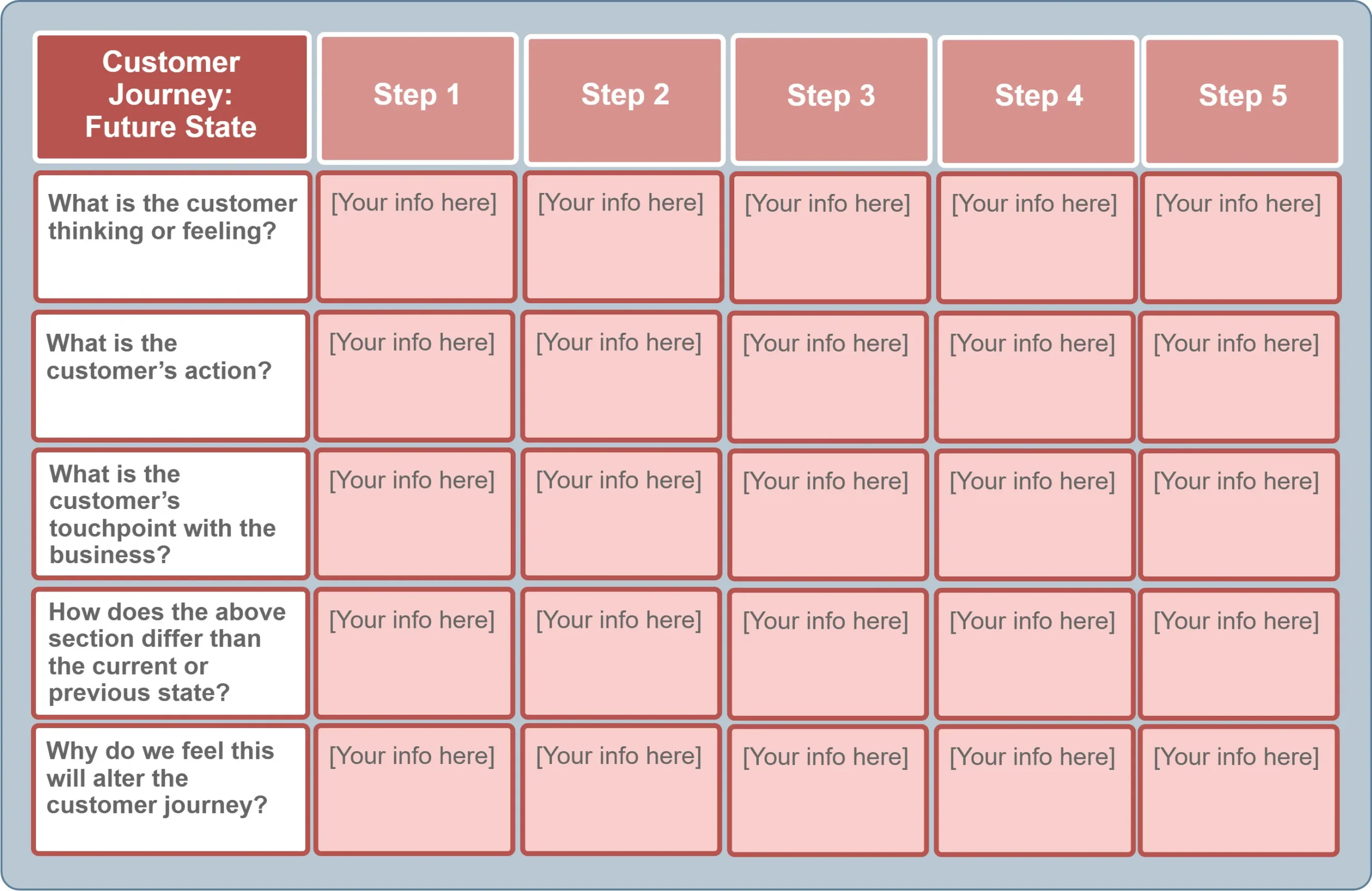
Future State CJM #
A separate template is used for the Future State, which includes:
- the customer’s emotions and motivation;
- the desired improvements in the interface and experience;
- KPIs for measuring the effectiveness of these changes.
In most cases, the buyer’s journey represents the current-state journey that customers go through today. Although there are likely some areas you are satisfied with, the current customer experience is rarely perfect or fully aligned with customer expectations. For example, customers may encounter obstacles while trying to achieve their goals. In other cases, there may be a higher-than-acceptable churn rate at specific stages, such as when using core product features or transitioning from a free version to a paid plan.
Reflects the desired state of the customer experience with the addition of new touchpoints and KPIs:
Desired emotions
Expected AI support
Level of personalization
Using a future-state customer journey map, you create a new map with new touchpoints and interactions based on your ideal vision. This way, you will know what needs to be done to build an optimal customer journey. If you have already experimented with creating customer journey maps and want to take the next step in improving customer experience quality, you will likely be interested in future-state mapping.
Future-State Template #
A future-state customer journey template allows you to describe the sequence of steps needed to create the most ideal customer journey possible.
A table to fill in includes:
- Emotions, actions, touchpoints, changes, and reasons for improvements.
You simply list the steps you want to take to create an outstanding customer experience and ask key questions about customer behavior.
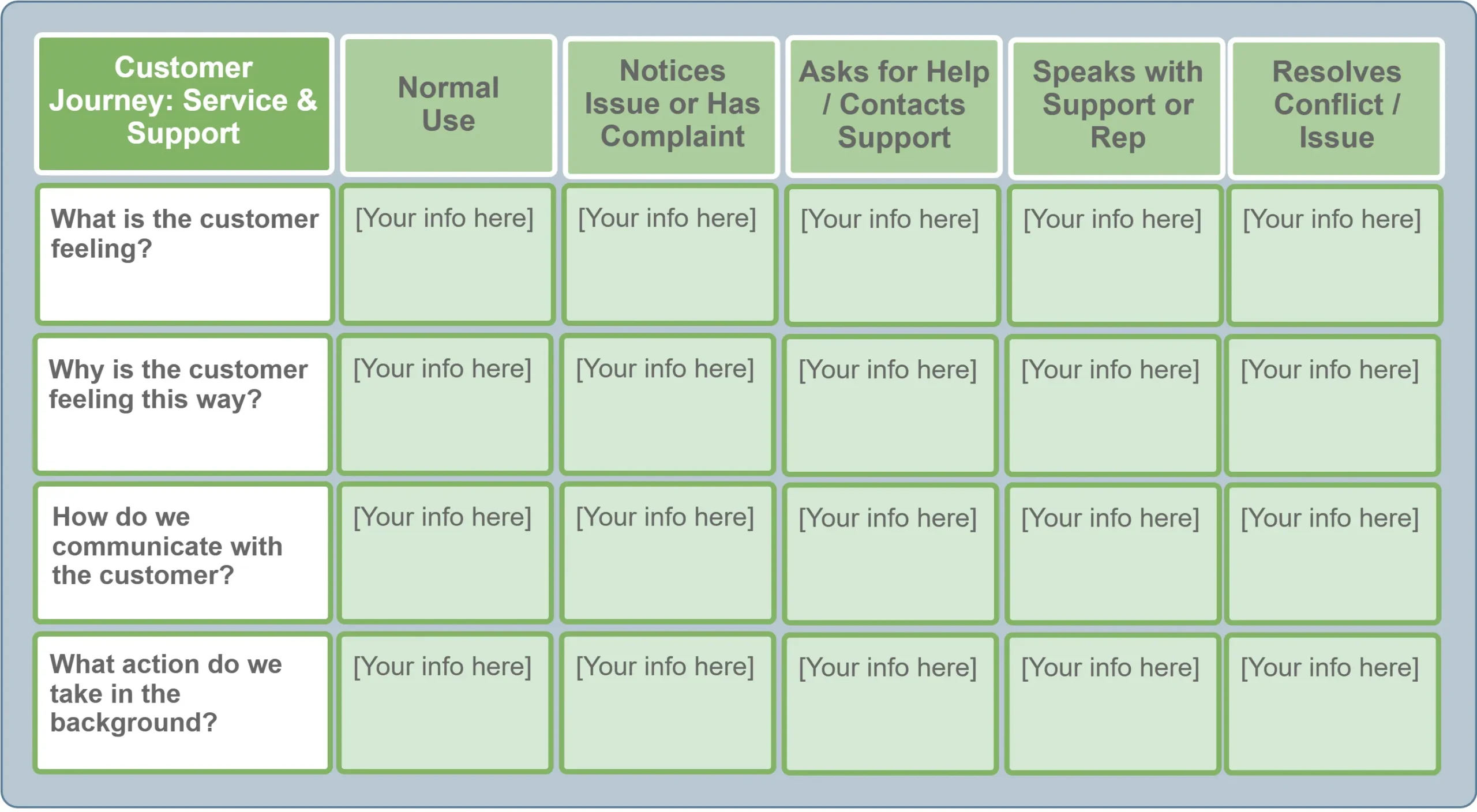
Customer Journey: Service & Support #
This CJM template is used to analyze the customer experience when contacting technical support — from the moment a problem arises to its complete resolution. It helps identify at which stages the customer experiences the most stress, where communication needs to be optimized, and which internal processes require improvement.
This CJM template is used to analyze the customer experience when contacting technical support — from the moment a problem arises to its complete resolution. It helps identify at which stages the customer experiences the most stress, where communication needs to be optimized, and which internal processes require improvement.
Template Structure #
Customer Journey: Service & Support includes five sequential stages that reflect a typical customer support journey:
| Stage | Customer Goal | Company’s Main Task |
|---|---|---|
| Notices Issue / Has Complaint | Notices a problem or malfunction | Reduce time to first contact |
| Speaks with Support or Rep | Communicates with an agent or AI bot | Give a clear explanation and show empathy |
| Resolves Conflict / Issue | Receives a solution | Confirm satisfaction and restore trust |
| Normal Use | Uses the product without issues | Maintain stability and proactive monitoring |
| Asks for Help / Contacts Support | Writes in chat, calls, or opens a ticket | Provide clear and fast access to support |
Key Parameters to Fill In: #
The template captures four core dimensions of interaction:
-

What is the customer feeling? #
Defines the customer’s emotions at each stage (calm, frustration, hope, satisfaction).
-

Why is the customer feeling this way? #
Clarifies the reason: complex interface, delayed response, unclear instructions, data loss, etc.
-

How do we communicate with the customer? #
Communication format: chatbot, email, phone call, callback, video assistance.
-

What action do we take in the background? #
Describes internal processes — escalations, automation, log analysis, ticket prioritization.
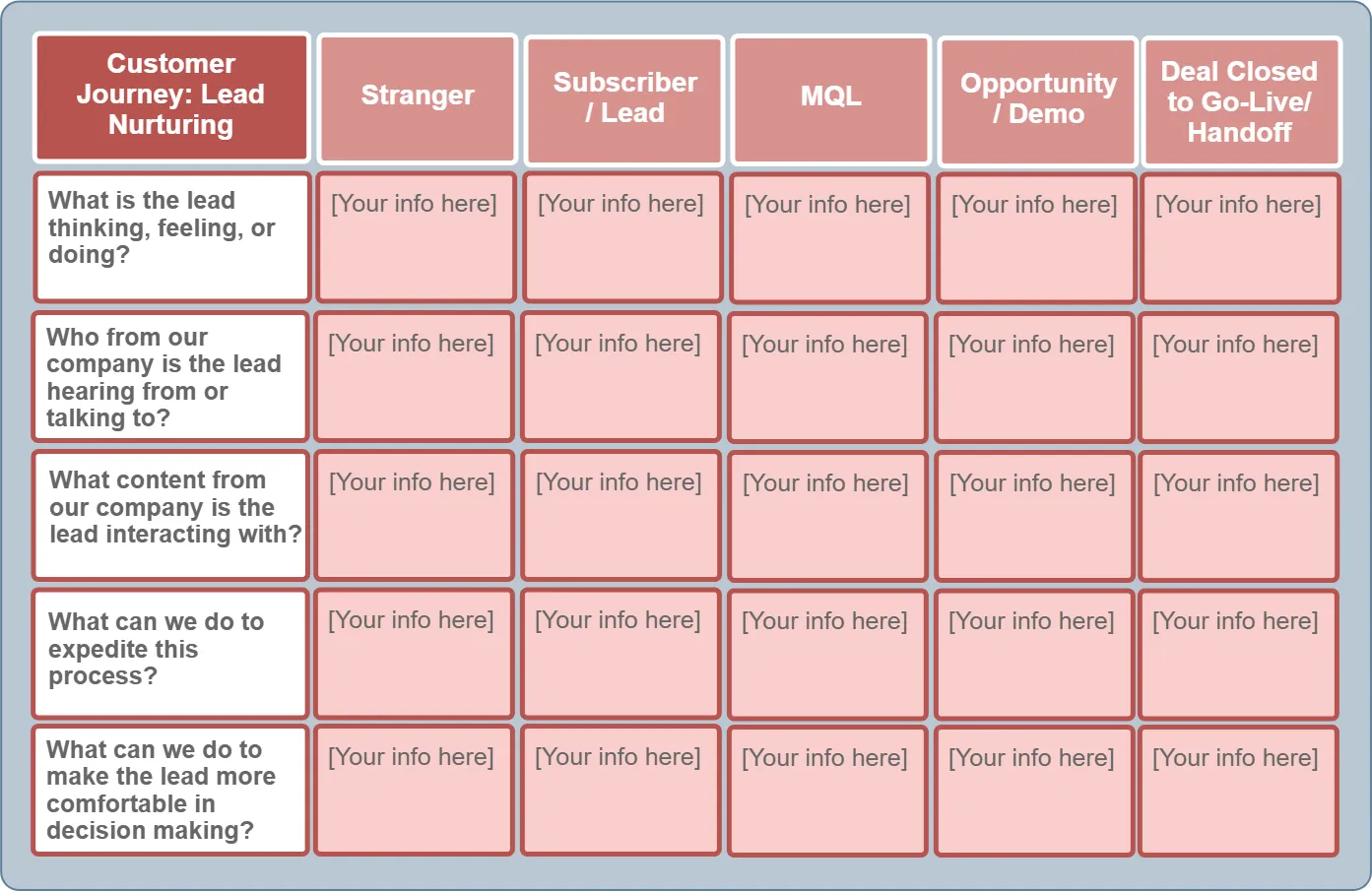
Lead Nurturing CJM #
Although technically this is part of the buyer’s journey, some marketers prefer to create a dedicated lead nurturing journey map because of the critical importance of lead nurturing. After all, any serious gaps in the lead nurturing process can undermine overall sales performance. And no matter how well your marketing team generates leads, the impact will be lost if you cannot successfully nurture them. To optimize this area of sales, you can create a lead nurturing journey map using a template like this.
Stranger → Subscriber → MQL → Opportunity → Customer
For each stage, the following are defined:
Lead emotions
The content they interact with
The people they communicate with
Tactical steps to accelerate conversion
Conclusion: #
A Customer Journey Map is not just a diagram. It is an interactive strategic thinking tool that brings together emotions, experience, and the effectiveness of interactions.
Customer journey mapping is a simple yet powerful way to comprehensively visualize every touchpoint along the user’s path for each buyer persona. Customer journey maps allow you to see how users move throughout the entire lifecycle — from the moment someone first becomes aware of your brand to the point of purchase and beyond. As we’ve learned, this serves several important purposes, including viewing the buying process from the customer’s perspective, identifying customer pain points, and uncovering opportunities to improve the customer experience at every stage.
The key is to follow best practices for building a customer journey map and to use the appropriate template to describe the buying process. Then, tracking key customer journey metrics — such as engagement, churn rate, and customer satisfaction — using analytics platforms like Woopra or Google Analytics should help you refine the customer journey map and fully optimize the customer experience.
For the U.S. bank account opening case, a CJM helps determine: #
Which stages build trust
Where the customer experiences doubt
Which touchpoints create value — and how to strengthen them using both digital and physical channels.
4. Unique Selling Proposition (Value Proposition Canvas as an Instrument) #

Purpose: #
- A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is a concise expression of a brand’s value that must simultaneously address customer needs and create a clear competitive differentiation.
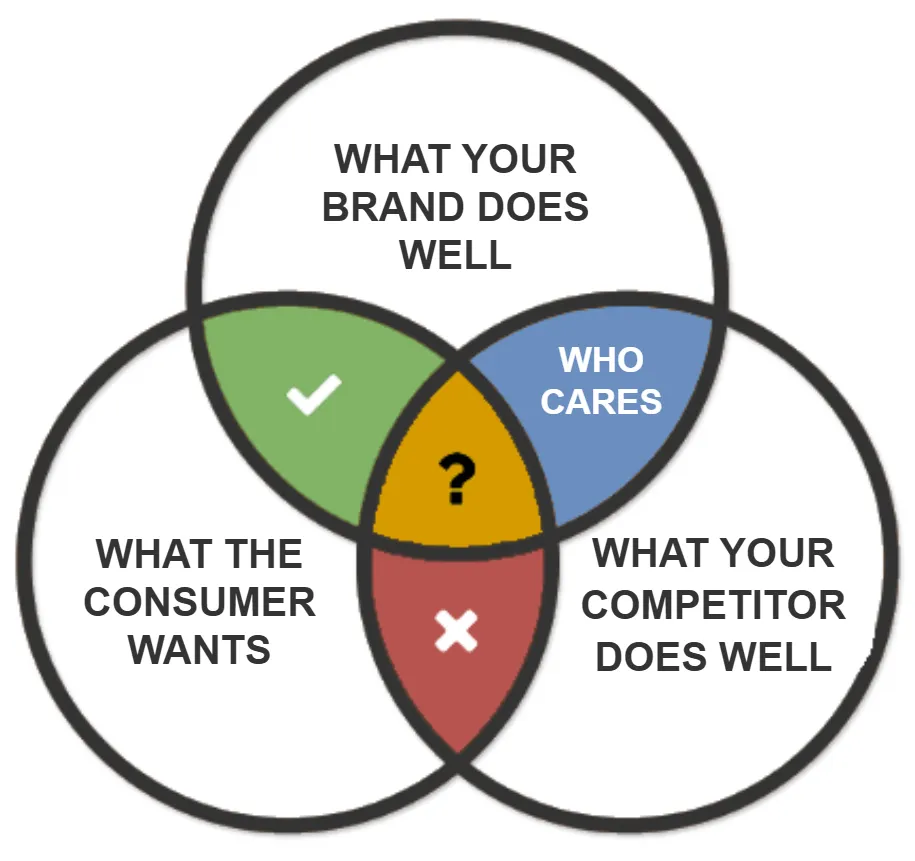
The formula for a successful USP is simple, but implementing it requires a nuanced analysis of three intersecting areas:
what the customer truly wants,
what the brand does well,
and what competitors are already offering.
Unlike general marketing positioning, a USP is the essence of the brand promise, expressed in a single phrase that serves as the foundation for the entire customer experience and all subsequent interactions with the product.

Why USP is important in the Research phase: #
- It turns the outcomes of Jobs-to-Be-Done and the Customer Journey Map into a concrete market offering.
- It helps focus communication and product priorities around real customer value rather than internal assumptions.
It serves as a bridge between customer needs (Jobs / Pains / Gains) and product functionality (Products / Pain Relievers / Gain Creators).
A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is the core of a brand’s positioning, reflecting why this particular product deserves the customer’s choice. Its purpose is not just to stand out, but to create a sustainable competitive advantage that simultaneously:
satisfies a specific customer need,
builds on the brand’s strengths,
and minimizes competitors’ influence in the overlapping area of interest.
USP Positioning Principle #
To identify such an advantage, the USP Positioning Principle is applied — an analytical principle that allows you to structure the market reality and determine where the brand truly wins. It is based on the intersection of three factors.
USP Strategic Zones: #
-
Winning Zone #
Clear point of difference that meets the needs. make it even bigger.
-
Losing Zone #
Your copetitor meets the consumer needs better then you do. you'll be crushed.
-
Risky #
Competitive battle ground. use emotion, innovative, su- perior execution.
-

Who Cares #
Many times, competitors battle in areas the consumer just doesn't care about. Have fun wasting your time.
These three factors create four strategic decision-making zones:
-

Winning Zone #
— the area of strong differentiation that addresses a significant customer need;
-
Risky Zone #
— a zone of competitive equilibrium that requires innovation or emotional differentiation;
-

Losing Zone #
— the area where competitors satisfy customer needs better;
-

Who Cares #
— aspects that are not important to the customer and do not create value.
Interpretation and Practical Recommendations #
This principle helps not only classify market positions, but also prioritize focus areas when shaping a value proposition and USP.
Focus on the Winning Zone: #
-
This is the territory where customer values and brand competencies align, and competitors have not yet reached it.
- Recommendation: Strengthen these directions — invest in communication, make it emotionally compelling, and create a strong sense of “only with us.”

Realistically Assess the Risky Zone: #
-
Here, competitors are also strong, and execution quality matters to the customer.
- Recommendation: Use emotional and UX-driven approaches to differentiate without resorting to price dumping. Innovation and service culture can become the decisive factors.

Avoid the Losing Zone: #
-
This is the trap where customers choose a competitor because their solution better addresses the need.
- Recommendation: Don’t try to “catch up” with the competitor — reconsider your focus. Sometimes it’s better to shift emphasis to a different segment or an innovative direction.
Don’t Waste Resources on the Who Cares Zone: #
-
A common team mistake is investing in features that do not matter to the customer.
- Recommendation: Regularly validate the importance of customer decision drivers (through Customer Insights, Jobs-to-Be-Done, or CJM analysis).
Practical Application for the U.S. Banking Case #
When developing a Unique Selling Proposition for the case of Emma, 29 — a Digital-First Millennial, this framework helps clearly filter out irrelevant arguments and focus on truly meaningful competitive advantages.
| Zone | Example for a Bank | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Risky Zone | Cashback bonus program | Differentiate through an ESG component |
| Winning Zone | Instant account opening and transparent pricing | Highlight in the USP and advertising |
| Losing Zone | Traditional branch-based services | Minimize investments |
| Who Cares | Complex pricing packages for narrow niches | Exclude from messaging |
Practical Value: #
- The USP Positioning Principle helps the team not only define “what we offer,” but strategically decide what is worth competing for and what does not deserve attention.
This analytical approach becomes the starting point for working with the Value Proposition Canvas, where the USP is translated into a concrete, operational form through the structure of: Jobs, Pains, Gains and Products, Pain Relievers, Gain Creators.
This principle allows teams at an early stage to eliminate non-essential directions, focus on valuable customer touchpoints, and build a conscious USP core, which will later be expanded within the Value Proposition Canvas.
From USP Strategy → to Value Proposition Canvas #
Once the team has defined its Winning Zone, the work moves to the next level — from a strategic principle to a tactical value modeling tool. If USP Zones help determine where we should compete, then the Value Proposition Canvas (VPC) answers the question:
To ensure that the transition from strategy to customer experience is structured and transparent, the tools — USP, Value Proposition Canvas, and Customer Journey Map — are aligned into a single logical value design architecture.
| Level | Tool | Key Question | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic | USP Positioning Principle | Where can we win? | Winning Zone and strategic differentiation point are defined |
| Operational | Customer Journey Map | Where does the customer experience this value in real interactions? | Touchpoints, interaction stages, and the customer’s emotional context are designed |
| Tactical | Value Proposition Canvas | How exactly do we create and deliver value? | Value proposition structure is formed: Jobs, Pains, Gains → Products, Pain Relievers, Gain Creators |

Practical Value: #
- In the Winning Zone, you define what gives the brand a tangible competitive advantage.
- Through the Value Proposition Canvas (VPC), you articulate how this advantage is embedded in the product.
- Through the Customer Journey Map (CJM), you demonstrate where exactly the customer experiences this advantage.
ARCHITECTURE OF VALUE DESIGN #
Strategic Layer #
Where can we win?
- Define the “Winning Zone”: the overlap between customer needs, brand strengths, and areas of low competition.
Feeds into Value Design Canvas.
Tactical Layer #

How do we create and deliver this value?
- Align customer Jobs, Pains, Gains with Product Features and Gain Creators.
Feeds into Value Proposition Canvas.
Operational Layer #
Where does the customer experience this value?
- Map out customer journey stages (Awareness – Advocacy) with emotions and touchpoints.
From Strategic Intent → to Value Design →

From Strategic Intent
to Value Design
to Customer Experience


Each tool builds upon the previous: USP defines what we promise, VPC defines how we deliver, CJM defines where the customer feels it.
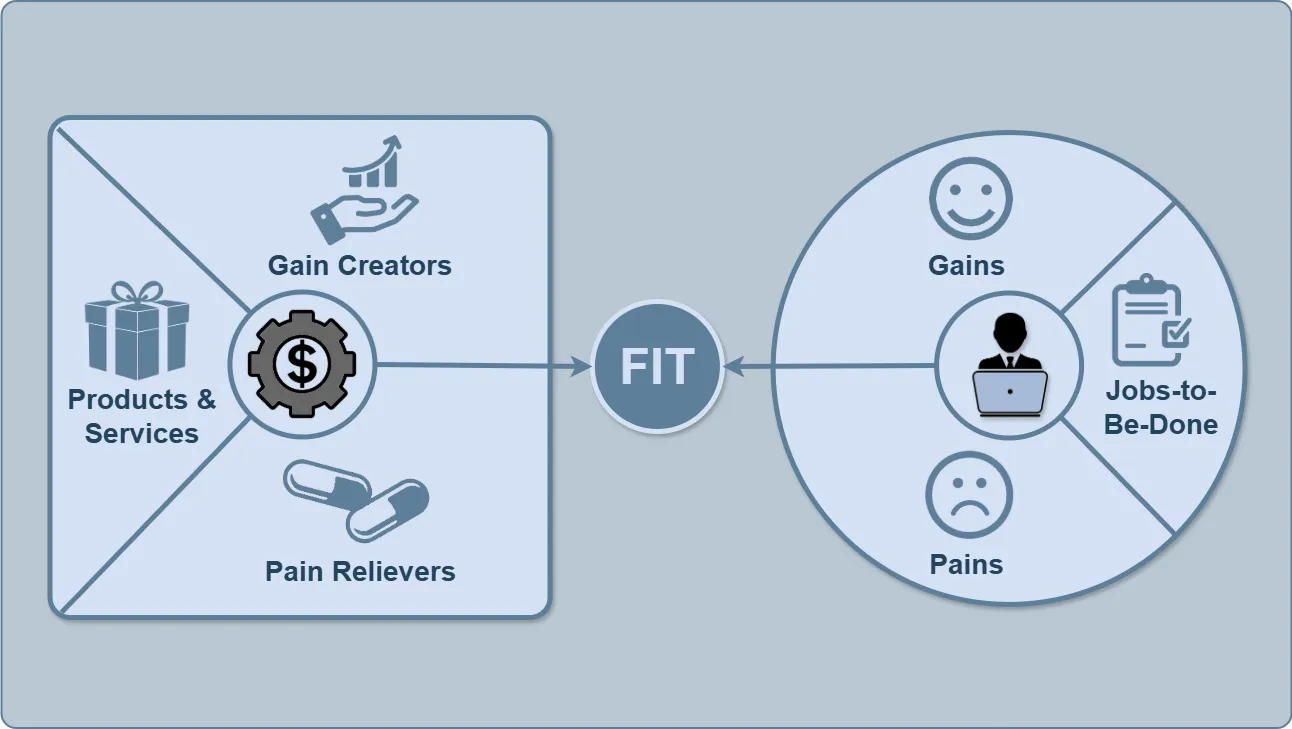
Methodology: Value Proposition Canvas #
The Value Proposition Canvas (VPC) is a visual framework that illustrates how a product creates value for a customer. It consists of two mirrored parts:
| Part | Content | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Profile | Jobs-to-Be-Done, Pains, Gains | Understand what the customer needs |
| Value Map | Products & Services, Pain Relievers, Gain Creators | Show how the product satisfies those needs |
| Strategic | USP Positioning Principle | Where can we win? |
At the intersection of these two parts, FIT is formed — the alignment between the product and customer expectations. From this intersection emerges the Value Proposition Statement, which then leads to a concise and compelling USP.
The goal of VPC is to ensure a perfect FIT between customer expectations and product value.
Application in the Case: Opening a Bank Account in the U.S. #
Persona #
-
values speed and control,
-
expects intuitive UX,
-
dislikes bureaucracy,
-
chooses companies with an ESG focus,
-
lives in a mobile ecosystem where everything should work “in three clicks.”
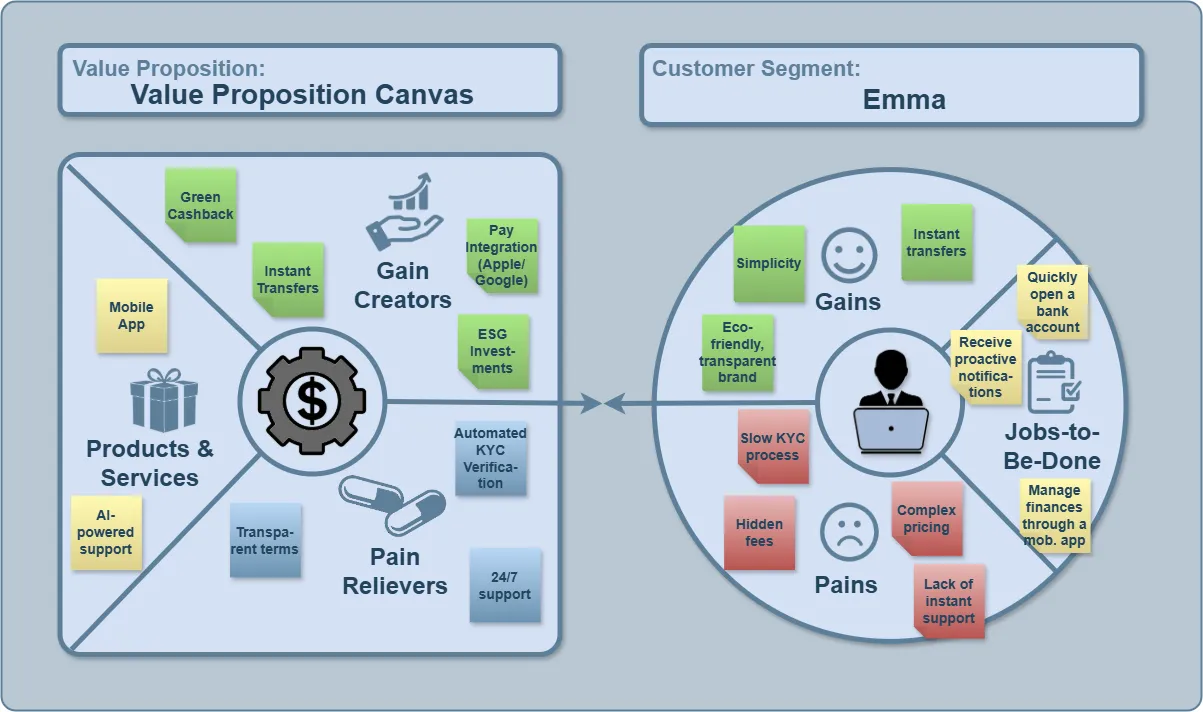
Practical Value Proposition Canvas Completion #
| Element | Content for the U.S. Bank Case |
|---|---|
| Pains | Slow KYC process, complex pricing, hidden fees, lack of instant support |
| Customer Jobs | Quickly open a bank account, receive notifications, and manage finances through a mobile app |
| Gains | Simplicity, instant transfers, eco-friendly and transparent brand image |
| Products & Services | Mobile app, multi-currency account, instant account opening, AI-powered support |
| Pain Relievers | Automated identity verification (AI-KYC), transparent terms, 24/7 chat support |
| Gain Creators | ESG investments, instant transfers, “green” cashback, Apple Pay / Google Pay integration |
Completed Value Proposition Canvas — Example from the U.S. Bank Case #

Customer Segment: #
- Emma is a Digital-First Millennial, placing a high priority on digital ease, transparency, and speed. Her key pains revolve around slow processes (like KYC), confusing pricing structures, and a lack of timely customer support.

Customer Jobs: #
- Emma wants to streamline her banking experience, ensuring she can quickly open an account, stay updated with notifications, and have complete control of her finances via a mobile app. Additionally, she seeks a seamless experience with quick access to financial products and services at her fingertips.

Gains: #
- Emma is attracted to simplicity, with a preference for instant financial transactions and a bank that aligns with her environmental and social values. She values transparency and efficiency, expecting clear communication and real-time updates about her financial activities.

Value Proposition: #
- The proposed solution for Emma's needs includes a multi-currency mobile app for easy account management and AI-powered support to ensure prompt responses. Pain points like slow KYC are relieved with automated verification, while transparency in pricing and constant support addresses other concerns. Additionally, ESG investments, instant money transfers, and integrations with payment tools like Apple Pay/Google Pay serve as key gain creators.
Value Proposition Statement and updated Unique Selling Proposition #
After completing the work with the Value Proposition Canvas, the final Value Proposition Statement is formed — a concise textual expression of the essence of the value proposition that connects the customer pain, the product’s opportunity, and the unique benefit.
This is done using the following format:
Example for our case — opening a bank in the U.S. #
Value Proposition Statement #
For international entrepreneurs and professionals who struggle to open a U.S. bank account quickly and manage compliance remotely, our banking platform “LibertyOne” is a hybrid U.S. banking service (digital + physical presence) that enables account opening in minutes, ensures full legal compliance, and provides smart AI-driven financial management with human support when needed.
Justification #
| Element | Source from VPC / CJM | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| “Digital” | Functional Gain | The ease of remote account opening and fund management through a mobile app. |
| “Human” | Emotional Gain | The combination of digital technologies and real support from an advisor builds trust and comfort. |
| “Compliant” | Gains (trust and security) | Legal transparency and automated regulatory compliance make the product reliable. |
| “Open in 3 minutes” | Jobs-to-be-Done and Pains | This addresses Emma’s key pain point — lengthy timelines and complexities of KYC/AML checks. |
| “U.S. business bank account” | Core Job | Emphasizes localization and the goal — specifically a business bank account in the U.S., not a general fintech platform. |
The Relationship Between USP and Value Proposition Statement #
- The Value Proposition Statement reveals the structure of the argument — who, why, what, and how is being offered.
- The USP is the verbal core of communication, a short and memorable formula that reflects the essence of the value.
From Value Proposition Statement → to USP → to Market Message #

(Analytical Layer)
Structured internal statement defining who the target customer is, their need, and how our solution delivers value.
- “For international entrepreneurs who struggle to open a U.S. bank account remotely…”
- Transforms analysis into a clear statement of value.

(Strategic Communication Layer)
Condensed, memorable core message combining function, emotion, and differentiation.
- “Open your U.S. business bank account in 3 minutes — compliant, digital, human”
- Strategic essence of the brand’s competitive position.

(Operational Communication Layer)
Customer-facing adaptation of the USP across marketing channels.
- “Start banking in the U.S. today — global entrepreneurs welcome.”
- Turns strategy into communication language.

From internal logic
to strategic essence
to market expression

Practical Tips for the Team #
Result of Implementation #
After implementing the VPC and formulating the USP, the team gets:
A clear language for customer communication,
A structured foundation for visual and advertising messages,
A focus on the real priorities of the target segment, not guesses.
VPC → USP Flow #

(Jobs / Pains / Gains)
Analyzing customer tasks, frustrations, and desired outcomes.
Job: Open U.S. bank account remotely
Pain: Bureaucracy, slow verification
Gain: Confidence, simplicity
Understanding Needs →
(Products / Relievers / Creators)
Designing how the product solves pains and creates gains.
Product: Hybrid bank LibertyOne
Pain Reliever: Online ID check
Gain Creator: AI-based financial assistant
Designing Value →

(FIT)
Defining the core communication promise – the FIT between customer and offering.
“Open your U.S. business bank account in 3 minutes — compliant, digital, human.”
Communicating promise
From customer understanding
through value design
to a clear promise