Topic Definitions
STEEP
DESTEP
Psychographics
MMM
Neural attribution

Sentiment AI

SO–WO–ST–WT hypotheses

Viral loops

Referral loops

Product triggers

Behavioral nudges

Automated attribution

W–T risk

Structure of Modern Marketing Analysis #
Modern marketing analysis within the Total Project Management Framework (TPmF) is not a standalone study, but a system of interconnected steps that progressively narrow the field of uncertainty —
from global trends and the macro environment to competitive strategy and growth tools.
Each step serves a specific purpose and forms the “input” for the next one.
The logic flows from:
Environment
Customer
Market
Strategy

Section 1. Macro Factors Analysis

Purpose:
- Understand the environment in which the project will operate.
- This stage identifies long-term trends and external forces that cannot be controlled but must be taken into account.
Key Tasks:
- Scan the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal contexts (PESTEL).
- Identify drivers and barriers that may reshape the market.
- Model development scenarios and assess their sensitivity for the project.
Tools and Methods:
-
PESTEL Analysis
a basic framework for analyzing the external environment.
-
Scenario Trend Scan (STEEP/DESTEP)
identification of long-term trends and early signals.
-
Cross-Impact Assessment
evaluation of how factors interact (e.g., how technological progress affects legislation).
-
Sensitivity Mapping
visualization of which scenarios are most risky or promising.
Outputs:
- A map of external factors and trends.
- Scenarios with probability assessment.
- A list of opportunities and threats (O/T) for integration into SWOT.
The results of this stage serve as the foundation for identifying market opportunities and risks in competitive analysis.
Section 2. Customers’ Needs & Unique Selling Proposition

Purpose:
- To develop an understanding of customers’ real needs and determine what makes the future product unique.
- If the first step described “the world around,” this one describes “the customer’s world.”
Key Tasks:
- Understand who the customers are and what matters to them.
- Identify the points where customer tasks overlap with product functions.
- Examine the emotional and cultural context of customer perception.
Tools and Methods:
-
Segmentation & Personas
identifying customer groups based on demographic, behavioral, and psychographic characteristics.
-
JTBD (Jobs To Be Done)
analyzing the context in which the customer “hires” the product to accomplish a task.
-
Customer Journey Map (CJM)
visualizing the customer’s path from need awareness to post-purchase experience.
-
Value Proposition Canvas (VPC) → USP
aligning customer pains and product value into a cohesive offering.
-
Vibe & Cultural Factors
emotional codes, cultural markers, and references that shape the brand’s “atmosphere.”

Outputs:
- Personas, JTBD maps, and a VPC with a validated Unique Selling Proposition (USP).
- Strengths and weaknesses of the product’s value (S/W for SWOT).
Customer expectation data becomes the basis for building positioning and conducting competitive analysis.
Section 3. Competitive Analysis & OSINT

Purpose:
- To define the market structure, the intensity of competition, and determine the project’s real position among other players.
- This is the moment of transition from an internal perspective (us and the customer) to an external one (the market and competitors).
Key Tasks:
- Build a map of market forces.
- Identify who dominates, who is growing, and who is losing ground.
- Reveal actual competitive differentiation.
Tools and Methods:
-

Micro-environment Mapping
mapping suppliers, partners, customers, substitutes, and competitors.
-
Competitive Map (Value–Price or Feature–Benefit)
visual comparison of players’ positions.
-

Porter’s Five Forces
pressure from suppliers, customers, substitutes, new entrants, and the level of intra-industry rivalry.
-
Extended Data-Driven SWOT Analysis:
deep SWOT with digital metrics and data analytics.
-

CSF (Critical Success Factors)
key success criteria in the market.
-

CPM (Competitive Profile Matrix)
comparing us and competitors across CSFs.
-
Competitive Polygon
visualization of strengths and weaknesses.
-

Integration of O/T
adding external factors from PESTEL.
-
Strategic SWOT Matrix (Analytical)
generating S–O, S–T, W–O, and W–T hypotheses.
-
Benchmarking & AI Analytics
analysis of digital data, trends, reviews, and attribution (MMM, neural attribution, sentiment AI).

Outputs:
- A map of the competitive landscape.
- Validated CSFs and SWOT hypotheses.
- Analytical hypotheses for strategic decision-making.
Customer expectation data becomes the basis for building positioning and conducting competitive analysis.
Section 4. Formulate Competitive Marketing Strategy

Purpose:
- To integrate everything obtained into a single vector of action — a strategy that defines how the project will win the market and grow.
- This is the bridge between analysis and practical management.
Key Tasks:
- Translate SWOT hypotheses into strategic decisions.
- Formulate goals, positioning, and growth approaches.
- Build a system for measuring and managing growth.
Tools and Methods:
-
Interpret Strategic SWOT Hypotheses → Strategic Goals
prioritizing hypotheses and setting measurable objectives.
-

Mission & Vision
defining the long-term purpose and the desired future state.
-

STP (Segmentation → Targeting → Positioning)
selecting target segments and building positioning.
-

Growth Strategy (Ansoff Matrix)
choosing growth scenarios: market penetration, product development, market development, diversification.
-
Growth Marketing System*
a systematic growth cycle: hypothesis creation, A/B tests, iterations, analytics.
-

Growth Hacking
a growth accelerator: short, low-cost experiments with high viral potential (referral loops, viral loops, product triggers, behavioral nudges).
-

Branding & Vibe Positioning
emotional brand identity, cultural code, product atmosphere.
-

Ethical & Sustainable Marketing
incorporating transparency, sustainability, and trust principles.
-
AI-Driven Measurement & Risk Framework
data-driven management: KPIs, automated attribution, W–T risk modeling from SWOT.
Difference Between Growth Marketing and Growth Hacking:
Growth Marketing
is a systematic growth process. where hypotheses, experiments, and A/B tests are built into a continuous cycle. It is part of the strategic block, forming a sustainable growth-management system.
Growth Hacking
is an experimental growth accelerator with minimal resources: testing hypotheses through unconventional, rapidly deployable tools. It is a “tactical booster” embedded within Growth Marketing as a specialized toolkit.

Outputs:
- Strategic Passport — a consolidated map of goals, segments, and approaches.
- Growth Map — a visual map of growth initiatives and experiments.
- KPI & Risk Dashboard — a panel of metrics and risk indicators.
These outputs transition into the implementation phase: Tactical Marketing (8P) and Marketing Communications.
Structure of Modern Marketing Analysis #
Each section logically follows from the previous one, and all outputs consecutively become inputs for the next level.

- СHAPTER 1 → Macro Factors → Opportunities & Threats (SWOT O/T)
- СHAPTER 2 → Customers & USP → Strengths & Weaknesses (SWOT S/W)
- СHAPTER 3 → SWOT + Strategic Matrix → Strategic Hypotheses
- СHAPTER 4 → Interpret SWOT Hypotheses → Strategy → KPIs → Execution
Decision Framework #
The Research phase in the Total Project Management Framework is designed to analyze the market environment, identify customer needs, assess competition, and shape strategic directions.
The project step Choose & Approve Research Methods helps stakeholders determine:
whether research is required,
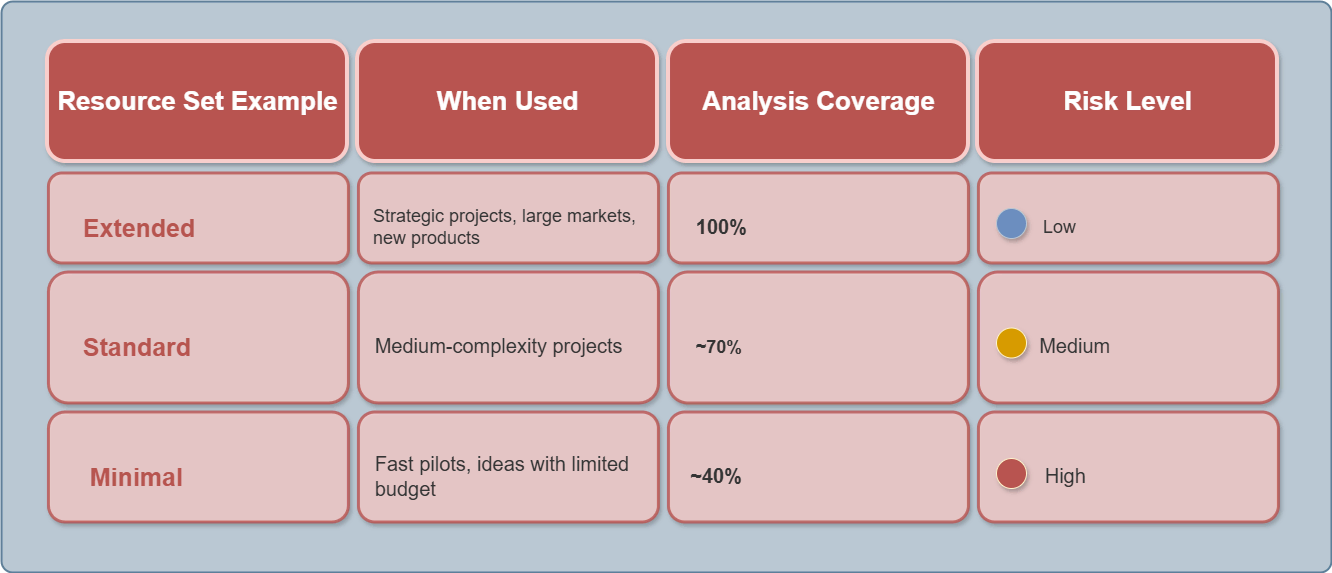
the appropriate scope (Minimal, Standard, Extended),
and what risks arise when the scope of analysis is reduced.
The system displays both the analysis coverage level (%) and the incompleteness risk (%), helping to find the right balance between research depth and available resources. It also shows how reducing the scope increases risk and suggests a minimal set of tools that can always be completed with the help of an AI assistant.
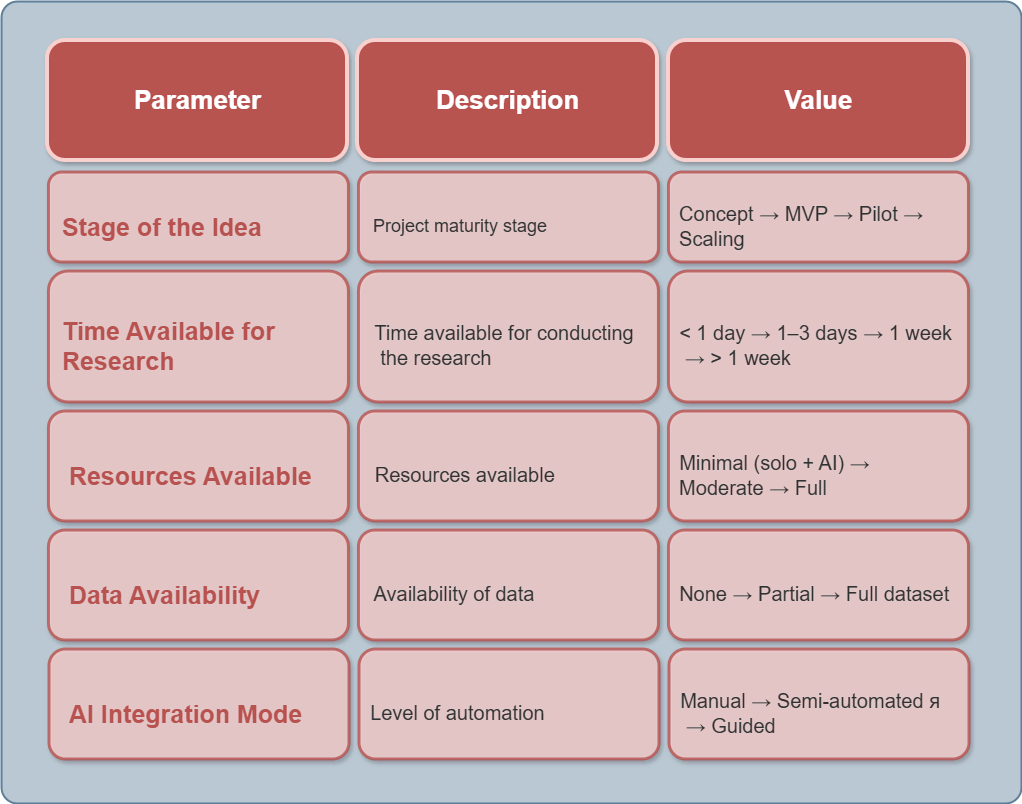
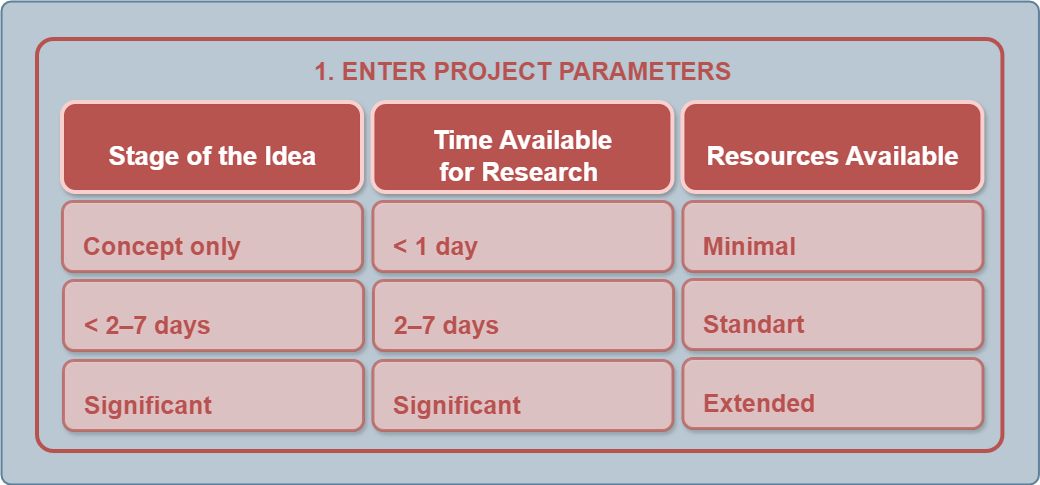
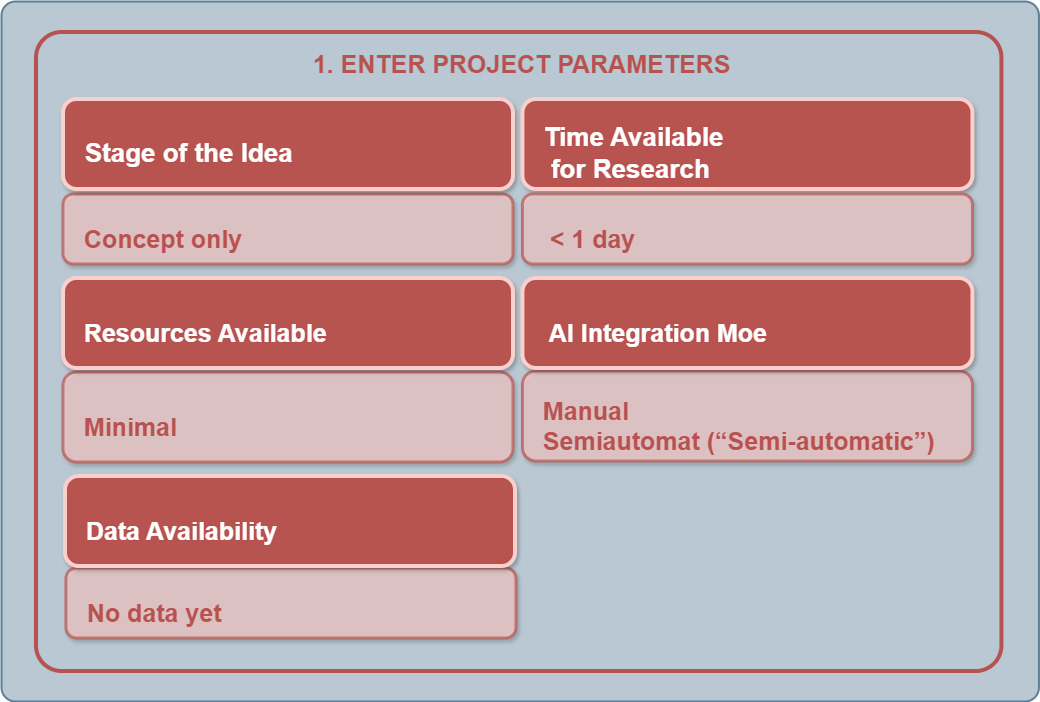
When selecting a Resource Set, three parameters are taken into account:
Time available for research.
Resources, including budget and data access.
Required decision accuracy (which defines the acceptable risk level).
Context of Use:
Purpose:
Step 1 — Define Research Parameters
The user enters the initial project parameters:
After the input is provided, the system calculates the Research Coverage level and displays the change in risk (Risk Compensation).
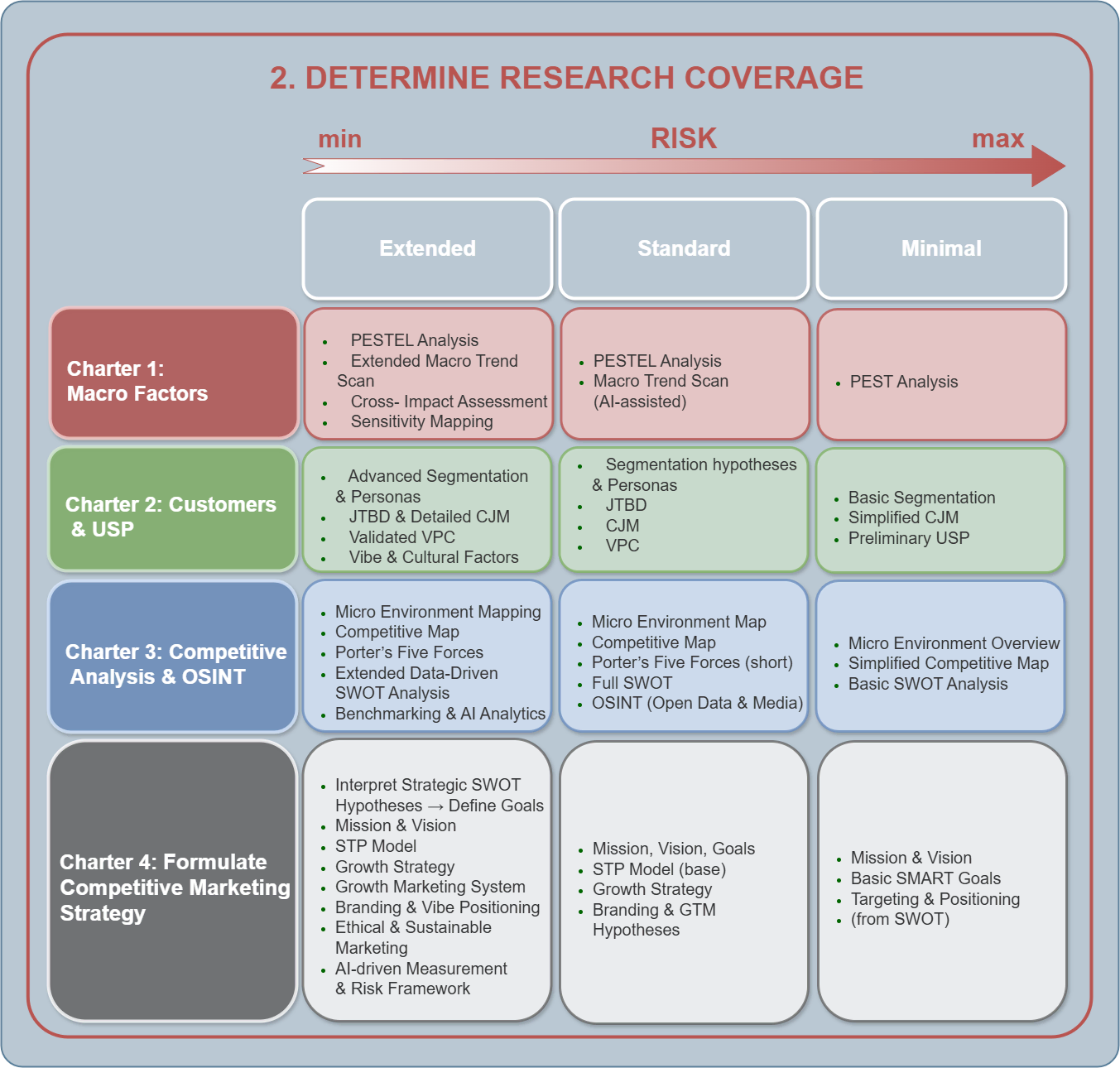
Step 2 — Determine Research Coverage
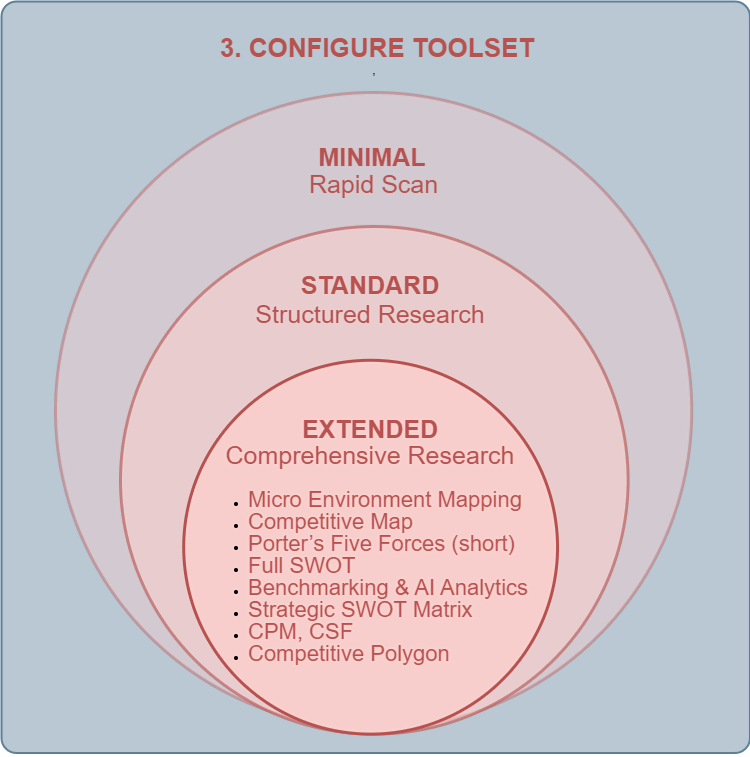
Step 3 — Configure Toolset
The research process consists of four sequential sections, each of which has three levels of analytical depth. The selected Resource Set determines the amount of data and the degree of detail within each section. Below are three examples of resource sets of different sizes — Extended, Standard, and Minimal — and an illustration of how they define the set of marketing analysis tools across the main sections.
Charter 1. Macro Factors Analysis
![]() Extended Resource Set:
Extended Resource Set:

Purpose:
- Identify global trends and factors that shape the project’s market context.
-
PESTEL Analysis
a full examination of political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors.
-

Extended Macro Trend Scan
scenario-based trend modeling (STEEP/DESTEP), detection of early signals.
-

Cross-Impact Assessment
analyzing interdependencies between trends (e.g., Tech–Legal, Eco–Social).
-
Sensitivity Mapping
assessing how sensitive the project is to different scenarios.

Outputs:
- Scenario Maps
- Sensitivity Matrix
- AI Dashboard
![]() Standard Resource Set:
Standard Resource Set:
-

PESTEL Analysis (short)
key macro factors.
-

Macro Trend Scan (AI-assisted)
major drivers and barriers.

Outputs:
- PESTEL Summary
- Trend–Impact Table
![]() Minimal Resource Set:
Minimal Resource Set:
-

PEST Analysis
political, economic, social, and technological factors.

Outputs:
- PESTEL Summary
- Trend–Impact Table
Charter 2. Customers’ Needs & Unique Selling Proposition

Purpose:
- Segmentation (Light)
- JTBD (Core Job)
- Unique Selling Proposition

Outputs:
- MVP, pitch deck, rapid hypothesis validation

- Segmentation & Personas
- JTBD (Jobs-To-Be-Done)
- Customer Journey Map (CJM)
- Unique Selling Proposition

Outputs:
- Go-to-market, product marketing, growth

- Segmentation & Personas
- JTBD (Jobs-To-Be-Done)
- Customer Journey Map (CJM)
- Unique Selling Proposition
- Vibe & Cultural Factors

Outputs:
- Deep product/brand insights, repositioning
Charter 3. Competitive Analysis & OSINT

Purpose:
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Competitive Map
- Basic SWOT Analysis

Outputs:
- Fast assessment, pre-sales, early-stage decisions

- Porter’s Five Forces
- Industry Mapping
- Competitive Map
- Data-Driven SWOT Analysis
- Strategic SWOT Matrix

Outputs:
- Corporate strategy, planning, go-to-market

- Micro Environment Mapping
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Industry Mapping
- Competitive Map
- Extended Data-Driven SWOT Analysis
- Strategic SWOT Matrix
- OSINT Benchmarking & AI Analytics

Outputs:
- In-depth analysis, investments, M&A, strategic transformations
Charter 4. Formulate Competitive Marketing Strategy

Purpose:
- Strategic Goals
- Mission (Light)
- Positioning (STP — Light)
- Core Growth Strategy

Outputs:
- Launch, focus, “here-and-now” decisions

- Strategic Goals (from SWOT)
- Mission & Vision
- STP — Segmentation → Targeting → Positioning
- Growth Strategy (Ansoff Matrix)
- Growth Marketing System
- Branding Positioning
- Measurement & Risk Framework

Outputs:
- Strategy + steady growth

- Interpret Strategic SWOT Hypotheses → Strategic Goals
- Mission & Vision
- STP — Segmentation → Targeting → Positioning
- Growth Strategy (Ansoff Matrix)
- Growth Marketing System
- Growth Hacking
- Branding & Vibe Positioning
- Ethical & Sustainable Marketing
- AI‑Driven Measurement & Risk Canvas

Outputs:
- Transformation, scaling, investments
The project step Choose & Approve Research Methods makes the Research phase manageable, transparent, and scalable.
Instead of a static marketing analysis, it forms a dynamic strategic thinking loop, where AI automates routine work and the user focuses on key decisions, approving them with a full understanding of context and risks.
Step 4 — Resource and Time Adjustment
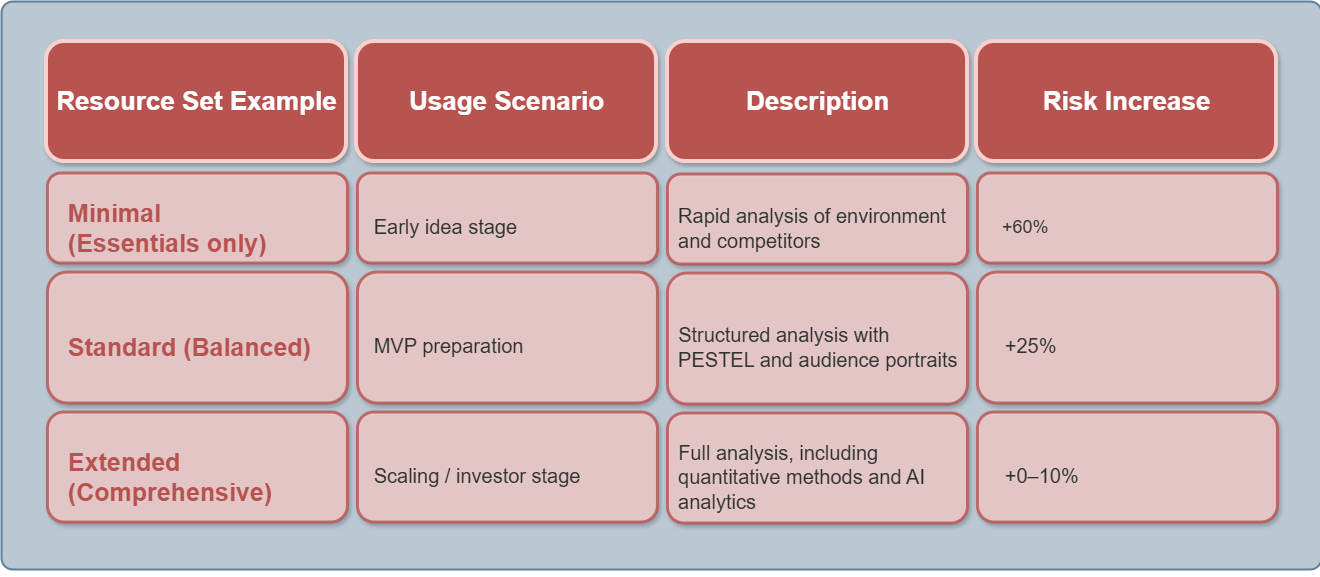
If resources are limited, the system offers a compromise:
-
Little Time
quantitative methods are excluded, only qualitative methods remain.
-
Limited Budget
AI replaces field research with secondary data.
-

Lack of Data
AI focuses on generating and validating hypotheses.
Each simplification is accompanied by a visual risk indicator:
Step 5 — Review and Approval Workflow
AI performs data collection operations, preliminary analytics, and automatic template filling.
The user reviews, edits, and approves each result.
This format ensures:
human control is maintained,
decisions remain transparent,
AI errors are eliminated through review.
Scenarios of Use #

1. Startup with Limited Resources
“+45% uncertainty. It is recommended to add market segmentation.”

2. Corporate Pilot Project

3. Scaling or Investor Stage
Results and Benefits #
Choose and Approve Research Methods makes the decision-making process:
-

intentional
risks and trade-offs are visible immediately;
-
adaptive
coverage is adjusted based on resources;
-

intelligent
AI handles routine work while the human approves the meaning;
-
universal
suitable for both startups and corporate teams.
Conclusion #
Modern marketing analysis is not a collection of methods, but a process of integrating data, insights, and decisions.
It enables a project not just to understand the market, but to design its own place within it.
Growth Hacking and Growth Marketing complete this chain, creating a bridge from strategy to continuous growth — from idea to a living product ecosystem.
What a stakeholder should remember when choosing a marketing analysis configuration:
-
Research
is not “just another document,” but a system of interlinked steps: each stage feeds the next.
-

Strategic SWOT Matrix
is a bridge between analytics and strategy: we generate hypotheses at Step 3, and then interpret and prioritize them at Step 4.
-
Communications
are only the tip of the iceberg; the reliability of decisions depends on the quality of the underwater part — research and strategy.
Choose and Approve Research Methods” is an intelligent filter between the idea and the analysis.
It does not replace the research — it transforms it into a manageable, transparent, and measurable process.
Each project receives its own optimal balance between speed and depth,
and the team gains a tool that makes research not a mandatory formality
but a meaningful part of the strategy.