Topic Definitions #
Iterative Approach

Iteration
Product Vision

MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
Feedback
Target Audience
Unique Value Proposition (UVP)

Early Adopters
Introduction to the Iterative Approach to Develop Product Vision #
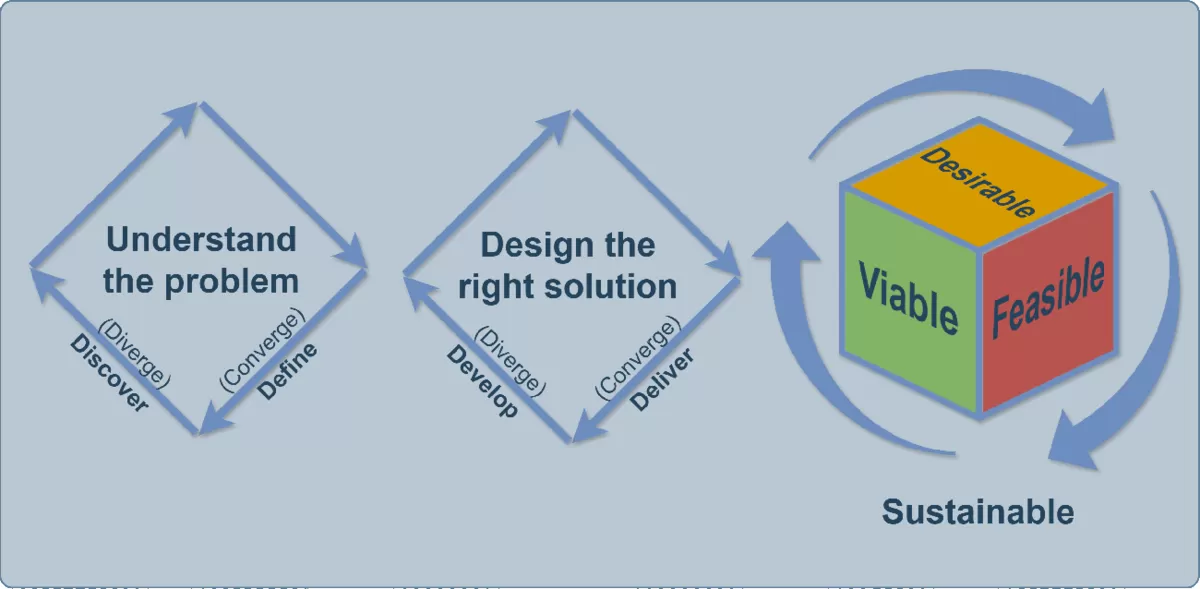
The iterative approach to product creation allows for systematically developing a product vision, starting from problem exploration and user neds identification to solution design and testing. This process, as shown in the image below, involves two cycles:
Understanding the Problem: This cycle consists of the “Discover” and “Define” stages, where the team collects data, analyzes current issues, and formulates the problem that needs to be solved.
Designing the Right Solution: This includes the “Develop” and “Deliver” phases, during which the team designs, tests, and implements the solution, delivering it to end users.
Key Principles:
Diverge
generating a wide range of possible solutions to the problem.
Converge
selecting solution from the proposed options based on analysis and feedback.
The goal of this approach is to create a viable, desirable, and feasible product that will remain sustainable in the long term.
Step 1: Product Vision Elevator Pitch #
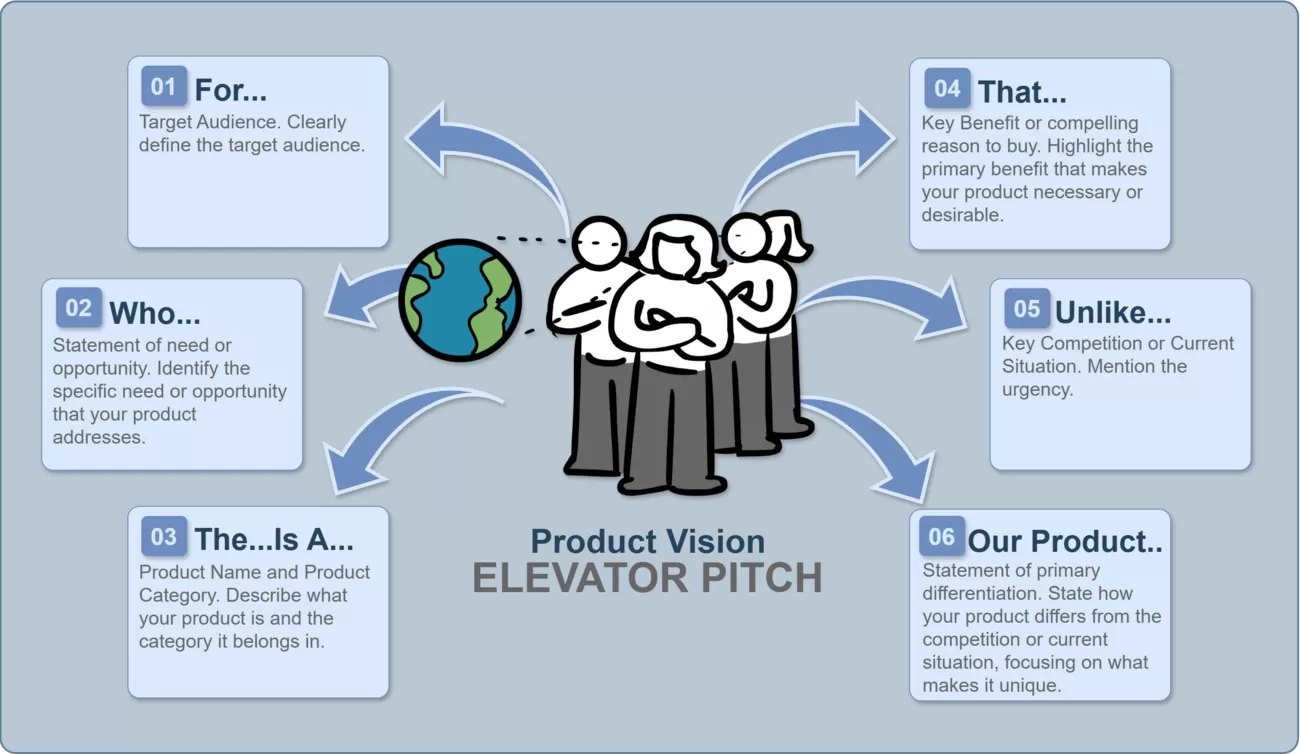
The first step in modeling the Product Vision is creating an Elevator Pitch. This tool helps to succinctly and clearly articulate the essence of your product. An Elevator Pitch is a brief and concise presentation of the product, designed to be delivered in a short amount of time (for instance, while riding an elevator). Its goal is to quickly explain the product’s essence, target audience, and benefits to capture the listener’s interest.
The image below shows a template for creating a Pitch:
-
For:
Define the target audience.
-
Who:
Describe the problem your users are experiencing.
-

The…is a:
Name the product and specify its category.
-

That:
Highlight the key benefit that makes the product essential.
-
Unlike:
Explain how your product differs from existing solutions.
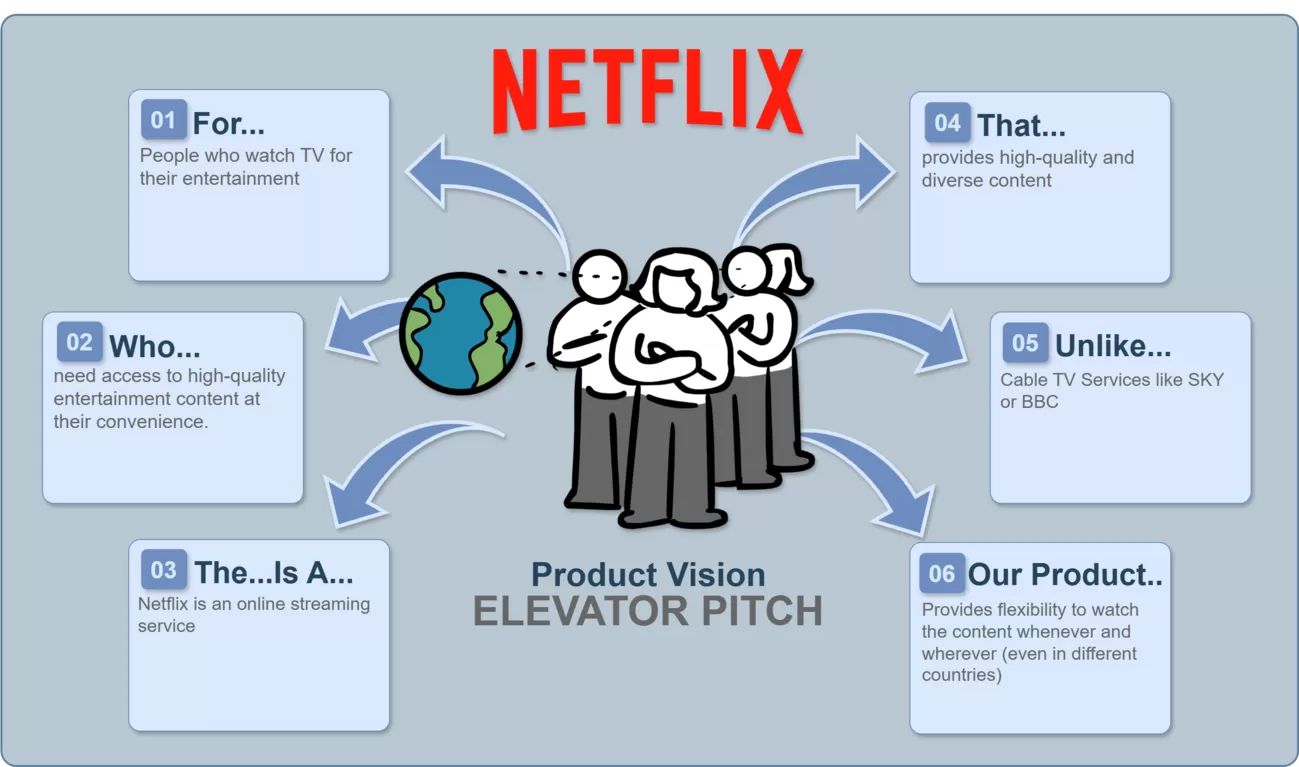
Example of Product Vision Elevator Pitch for Netflix:
This step helps to create a basic understanding of the product and communicate it to stakeholders.
Step 2: Product Visualization (Product Box) #
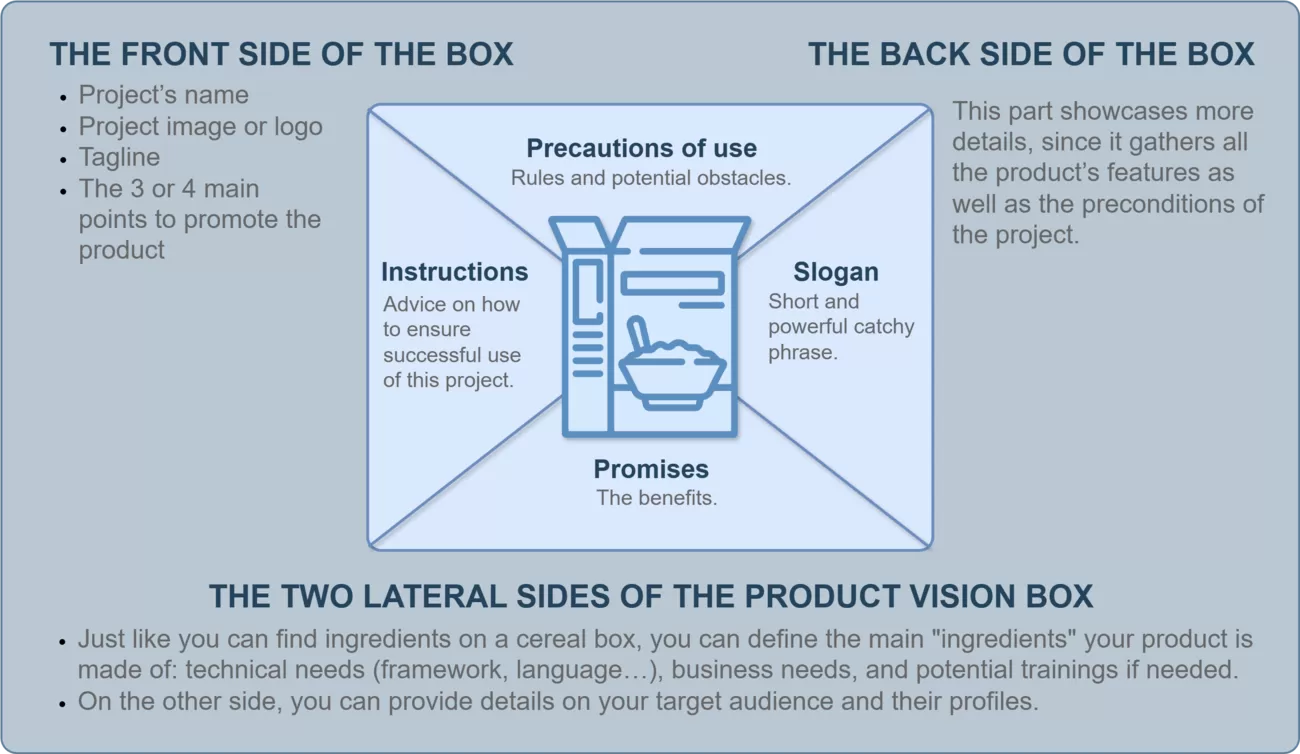
The next step is visualizing the product through the Product Box method. This exercise, shown in the third image, helps the team design a “box” for the product, imagining it as if it were being sold in a retail store. It focuses on key product features that matter most to customers.
Key elements of the Product Box:
-

Front Side:
Contains the product name, logo, and key benefits the team wants to emphasize.
-

Back Side:
A more detailed description of the product’s features and usage conditions.
-

Lateral Sides:
List the technical and business needs, the target audience, and user profiles.
Step 3: Decomposition via Lean Product Canvas #
Lean Product Canvas (fourth image) is a tool for deeper product analysis. It helps structure the key elements of the vision. Lean Product Canvas is a tool for creating a product’s business model, helping structure and visualize key aspects such as user problems, solutions, unique advantages, target audience, and key success metrics:
-

Problem:
Define the top 3 problems users face.
-
Solution:
The top 3 features that solve these problems.
-

Unique Value Proposition:
A clear statement of why your product is special and worth choosing.
-

Key Metrics:
Determine the metrics by which the success of the product will be measured.
-

Existing Alternatives:
List current market solutions and how your product will compete with them.
-
Channels:
The ways in which the product will reach end users.
-

Early Adopters:
Characteristics of early users who will help test the product.
This step allows the team to translate ideas into actionable steps and determine the key factors for success.
Step 4: Product Vision Evolution through Iterations (MVP and Feedback) #
In the final step (fifth image), the iterative process of refining the product happens through creating an MVP (minimum viable product) and gathering feedback from users.
Key points:
-

Definition:
The initial phase of defining and planning the product.
-

Execution:
Prototyping, testing solutions, and collecting feedback.
-
Iteration:
Constant improvement of the product based on user data.
This process helps build a product that solves real user problems and becomes more effective with each iteration.
Conclusion #
Developing a Product Vision is an iterative and evolving process that bridges creativity with systematic validation. It begins with simple tools like the Elevator Pitch, which helps teams articulate the product’s essence, target audience, and value proposition. As the process advances, visualization techniques such as the Product Box make abstract ideas tangible, ensuring alignment among stakeholders and clarity on the product’s key benefits and features.
The Lean Product Canvas then deepens the analysis by mapping out the problem, solution, value proposition, customer segments, and revenue model, offering a holistic perspective of the business model behind the product. Finally, through iterations and MVP development, teams refine their assumptions, collect feedback, and continuously improve the product to meet user needs more effectively.
This approach ensures that the product remains viable, feasible, and desirable, aligning user expectations with business goals. By combining structured frameworks with iterative learning, teams can reduce uncertainty, focus on delivering real value, and build products that are both sustainable and impactful in the long term.