Topic Definitions #
Roadmap
Jira Product Discovery

Waterfall Method
Mind Map
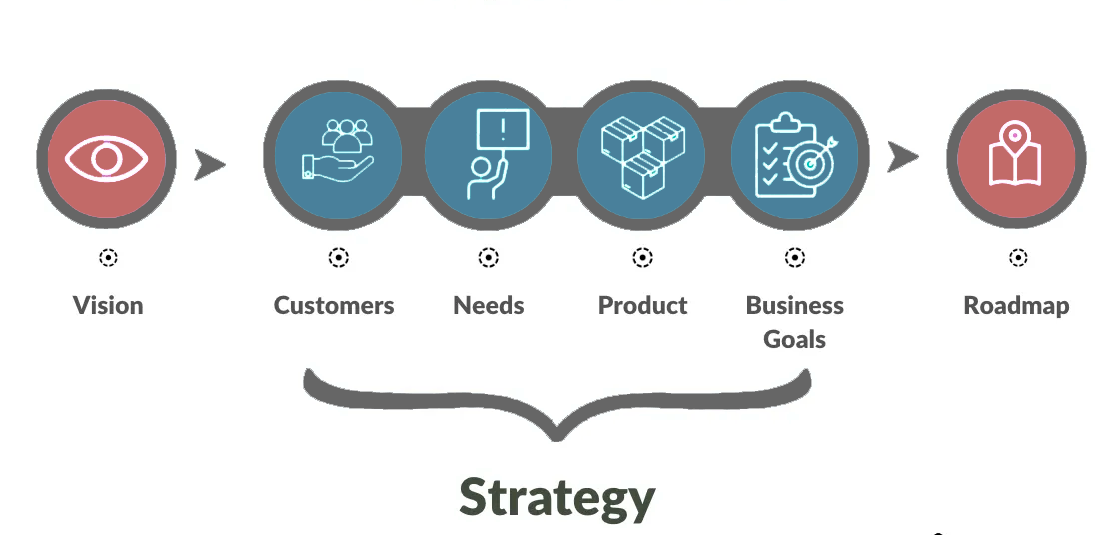
Develop Road Map: The Foundation for Successful Project and Product Management #
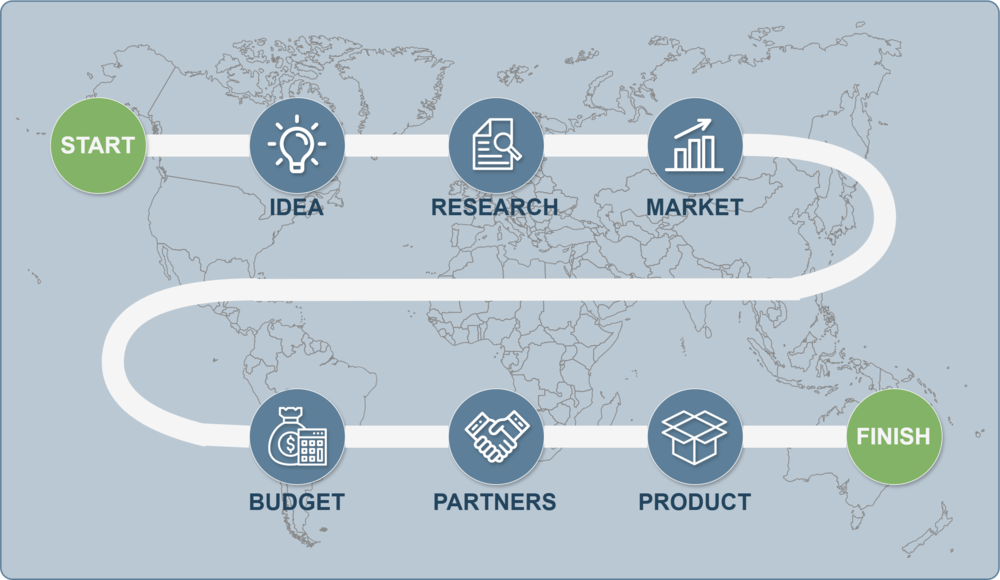
The Product Roadmap helps the team clearly set priorities, allocate resources, and track progress while keeping a focus on outcomes that meet user needs and market demands. It includes product features, planned improvements, new releases, and strategic goals that guide the team toward achieving long-term results as part of the effort to Develop Road Map.
In contrast, the Project Roadmap focuses on organizing the project’s work: breaking it down into phases, defining dependencies, setting deadlines, and monitoring completion. Both roadmaps complement each other, forming a unified vision and allowing teams to Develop Road Map strategies holistically.
Develop Road Map: Iterative Development and Gamification of the Process #
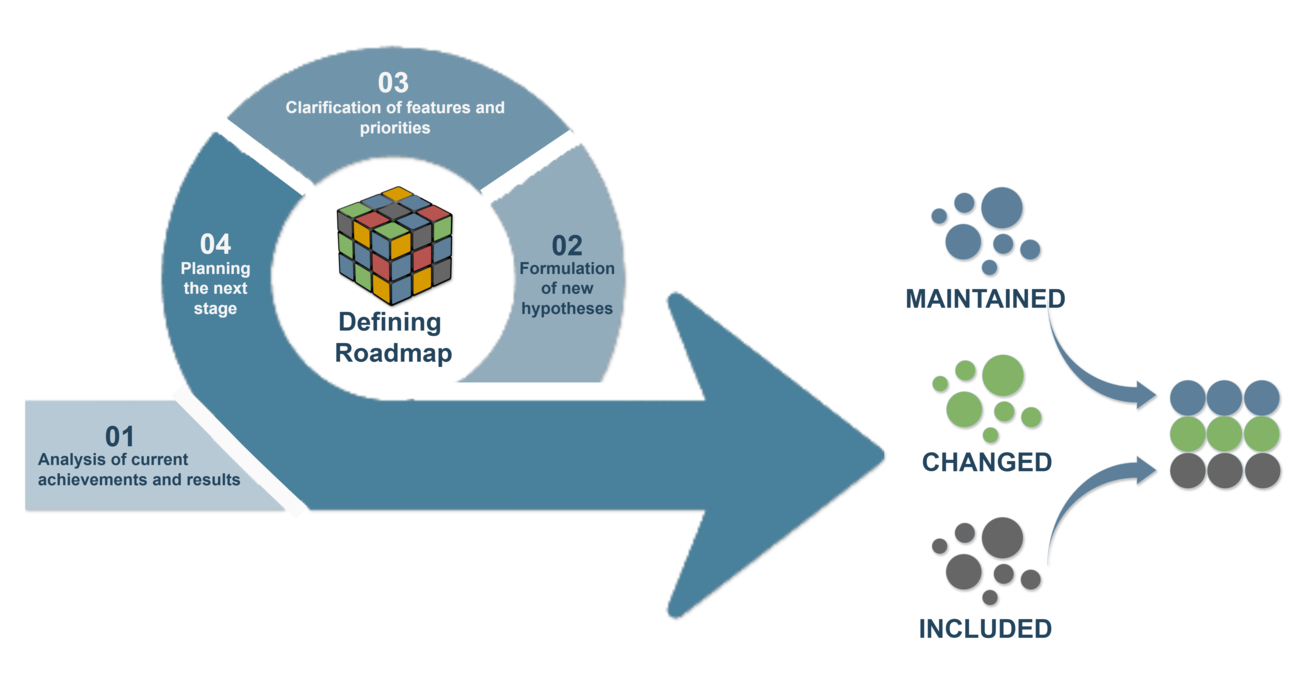
The iterative approach to roadmap development allows teams to quickly adapt to new data and project changes. Unlike the rigid waterfall method, which follows a fixed plan, this process encourages continuous feedback, adaptation, and hypothesis testing at every stage to Develop Road Map that responds to change.
Each iteration includes the following steps in the process to Develop Road Map:
-
Analysis of current achievements and results:
At the end of each iteration, the results of the achieved goals are evaluated, and adjustments are made if necessary to refine the Develop Road Map.
-
Formulation of new hypotheses:
Based on feedback from users and stakeholders, new hypotheses are developed for further testing in the next stage of the Develop Road Map.
-
Clarification of features and priorities:
After analyzing the hypotheses, decisions are made on which product features should be implemented first and how they fit into the overall strategy outlined in the Develop Road Map.
-
Planning the next stage:
The team defines new tasks, sets deadlines, and assigns resources for the next iteration, continuing to Develop Road Map based on evolving needs.
This methodology is especially important in unstable market conditions, where flexibility and readiness for change are essential for success. The iterative process allows teams to respond promptly to new data and ensures that product development remains relevant and aligned with user needs.
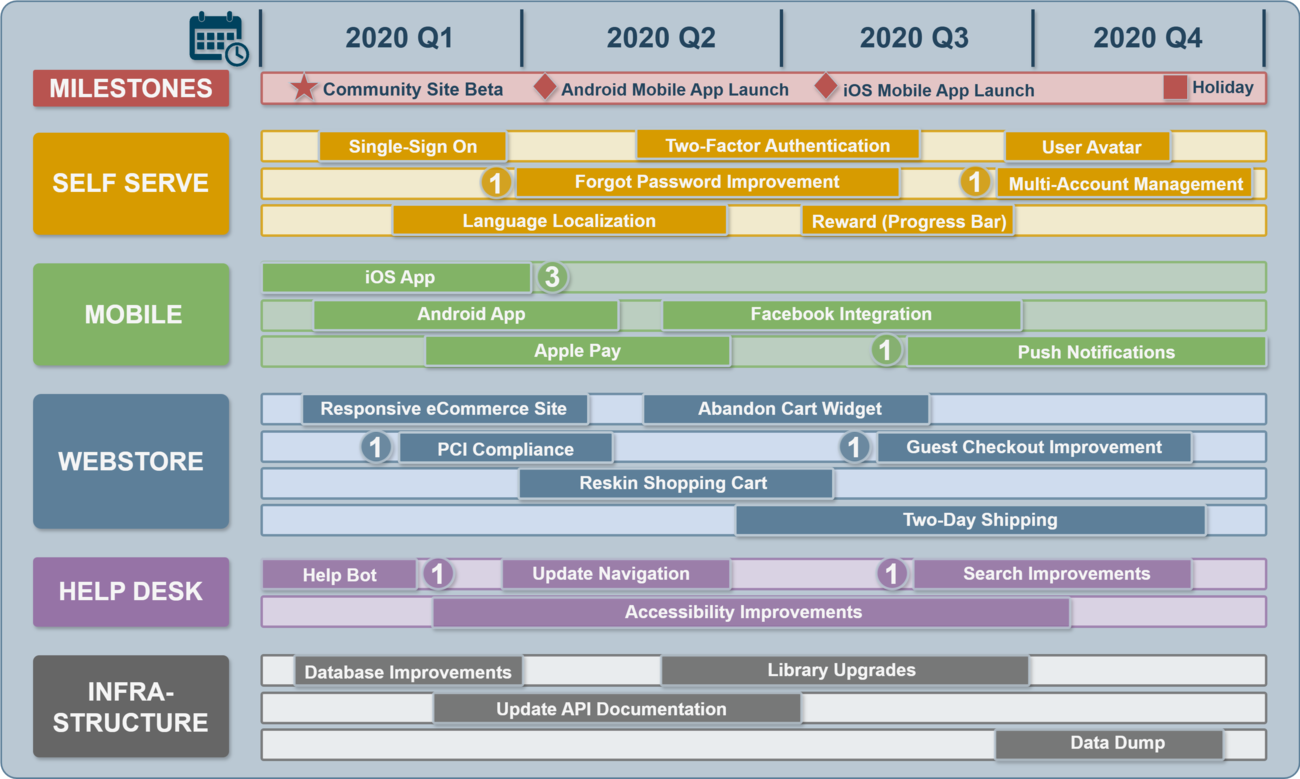
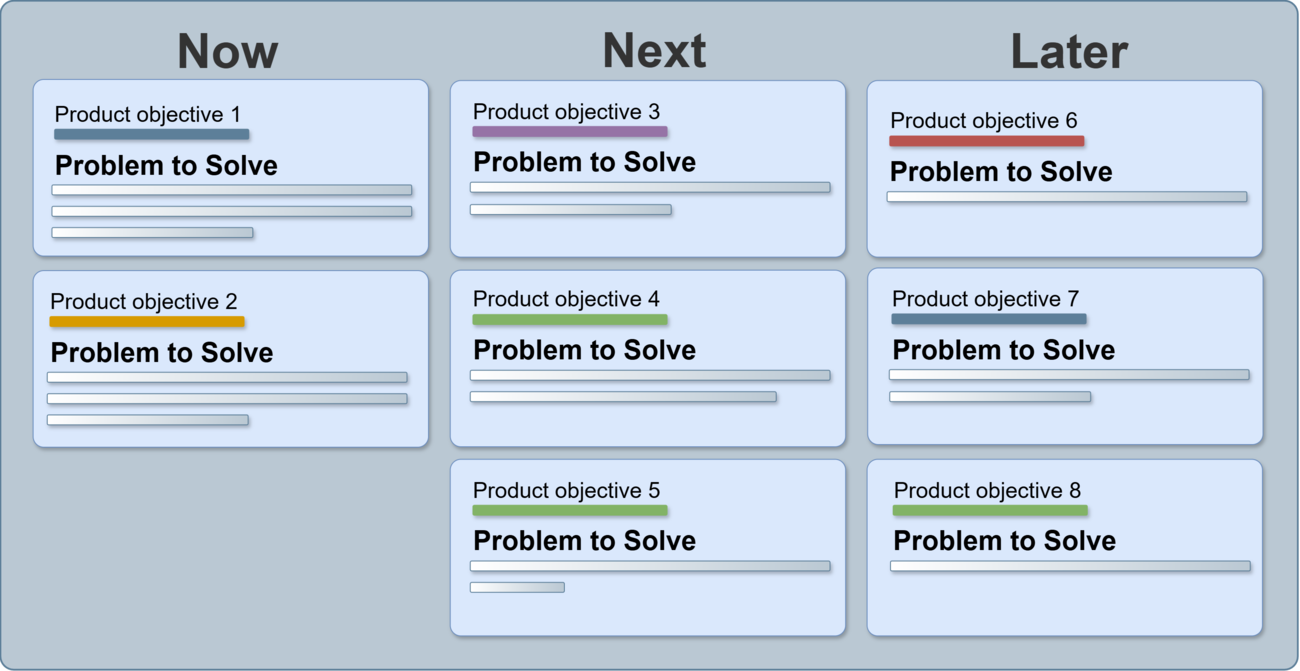
Product Roadmap: Structure and Key Elements in the Develop Road Map #
The Product Roadmap is a strategic plan that reflects the long-term vision of product development. Its main task is to show how the goals will be achieved through step-by-step feature implementation, based on priorities already determined during hypothesis testing and idea ranking.
Key elements of the Product Roadmap include:
Product milestones:
- These mark the key stages of product development. As teams Develop Road Map, they align launches with strategic objectives.

Functional blocks:
- Define specific features or improvements to be implemented per iteration. Prioritization is essential to successfully Develop Road Map.
Feedback cycles:
- Crucial for adjusting and improving the roadmap as needed. Teams use feedback to refine the approach and Develop Road Map iterations.
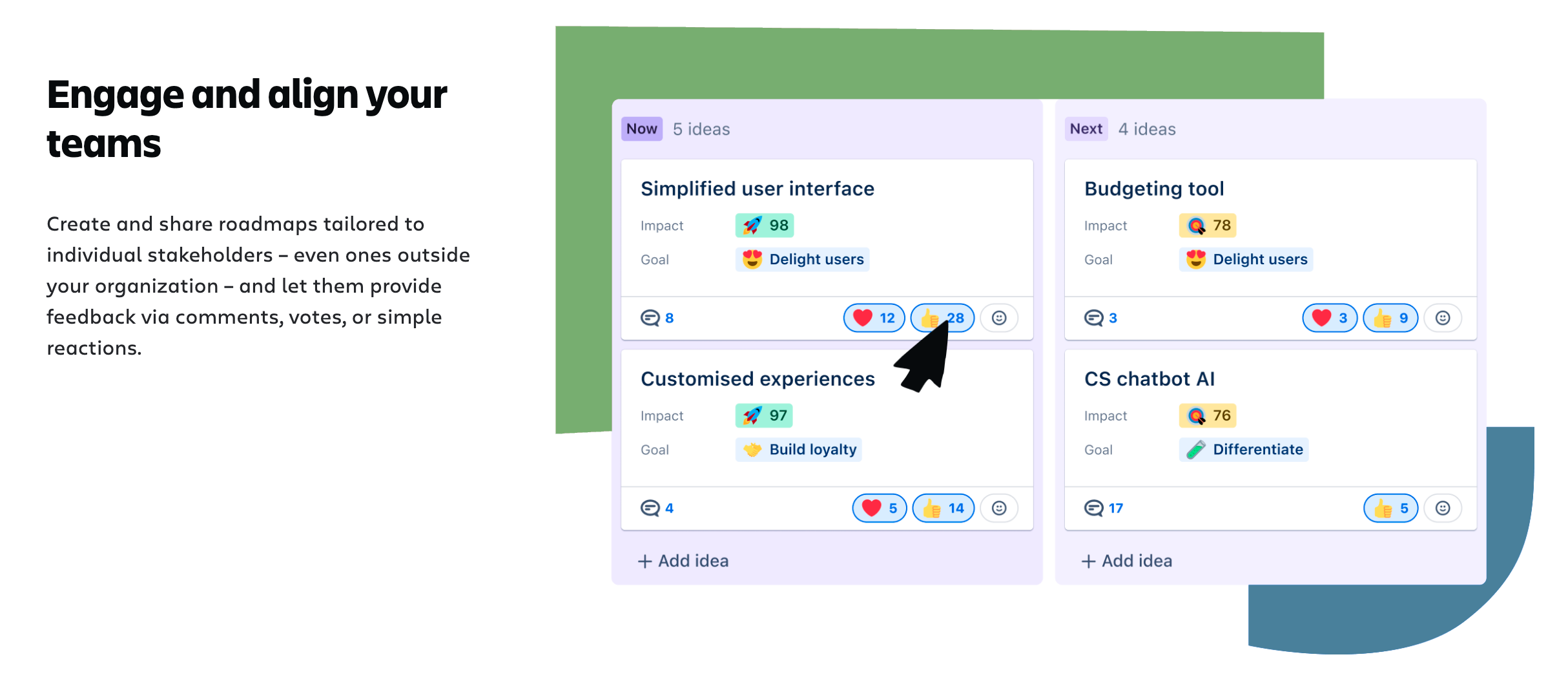
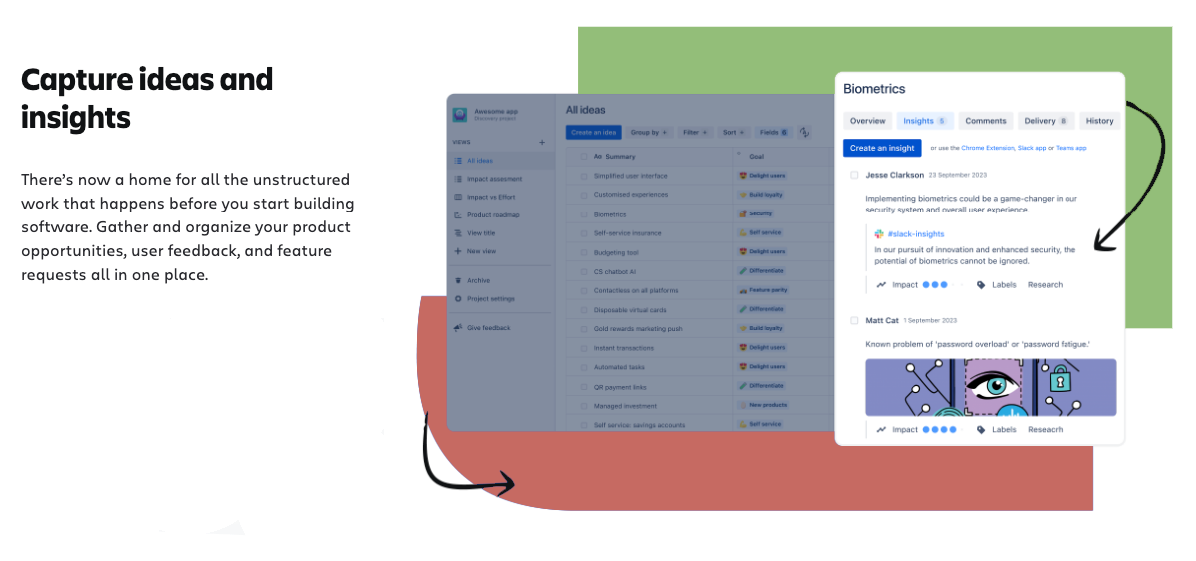
Integration of Jira Product Discovery to Develop Road Map Efficiently #
Jira Product Discovery enables teams to integrate ranked ideas directly into the Project Roadmap, optimizing development. Assigning ideas to specific phases enhances transparency and improves workflow when teams Develop Road Map.
With features like team voting, impact analysis, and effort estimation, Jira ensures better prioritization of tasks in the Develop Road Map process.
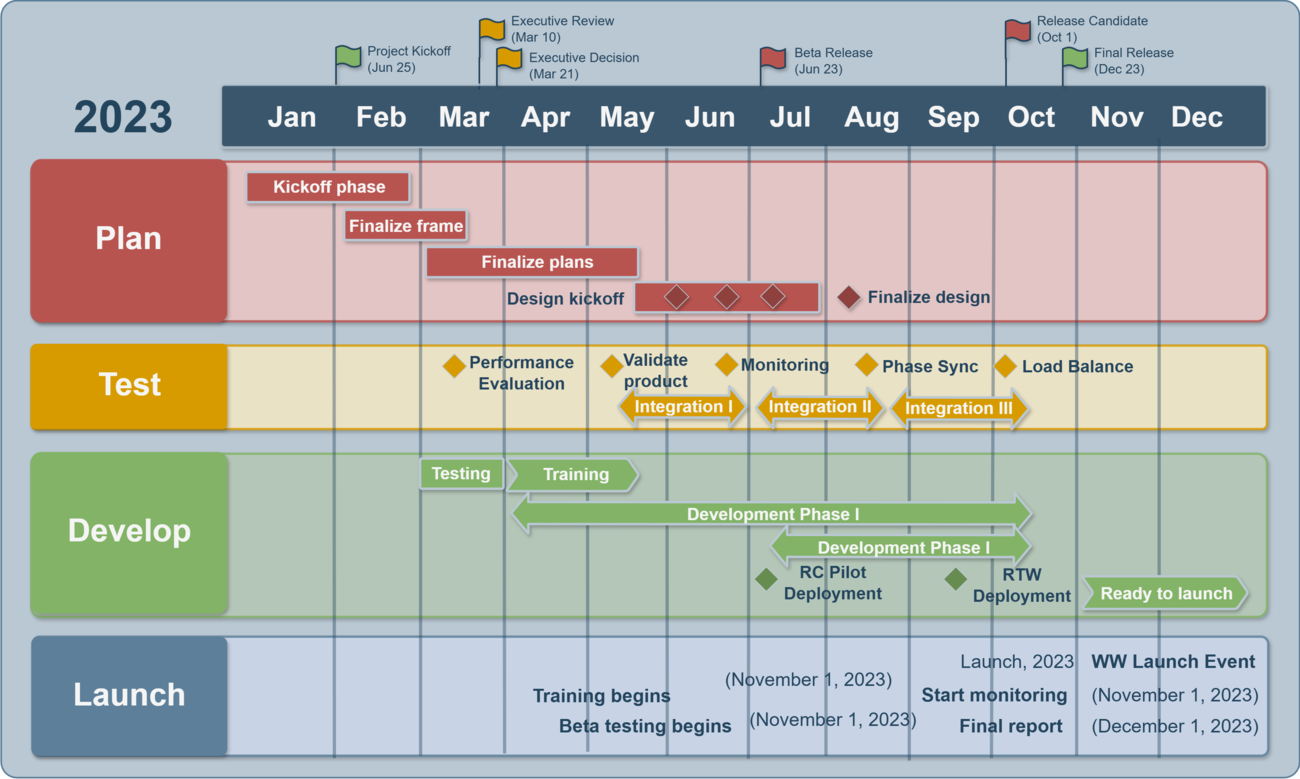
Project Roadmap: Structure and Phases #
The Project Roadmap plays a key role in project management, ensuring the organization of tasks, timelines, and control over the completion of key stages. This tool defines how the product strategy, outlined in the Product Roadmap, will be implemented and allocates resources to achieve the goals.
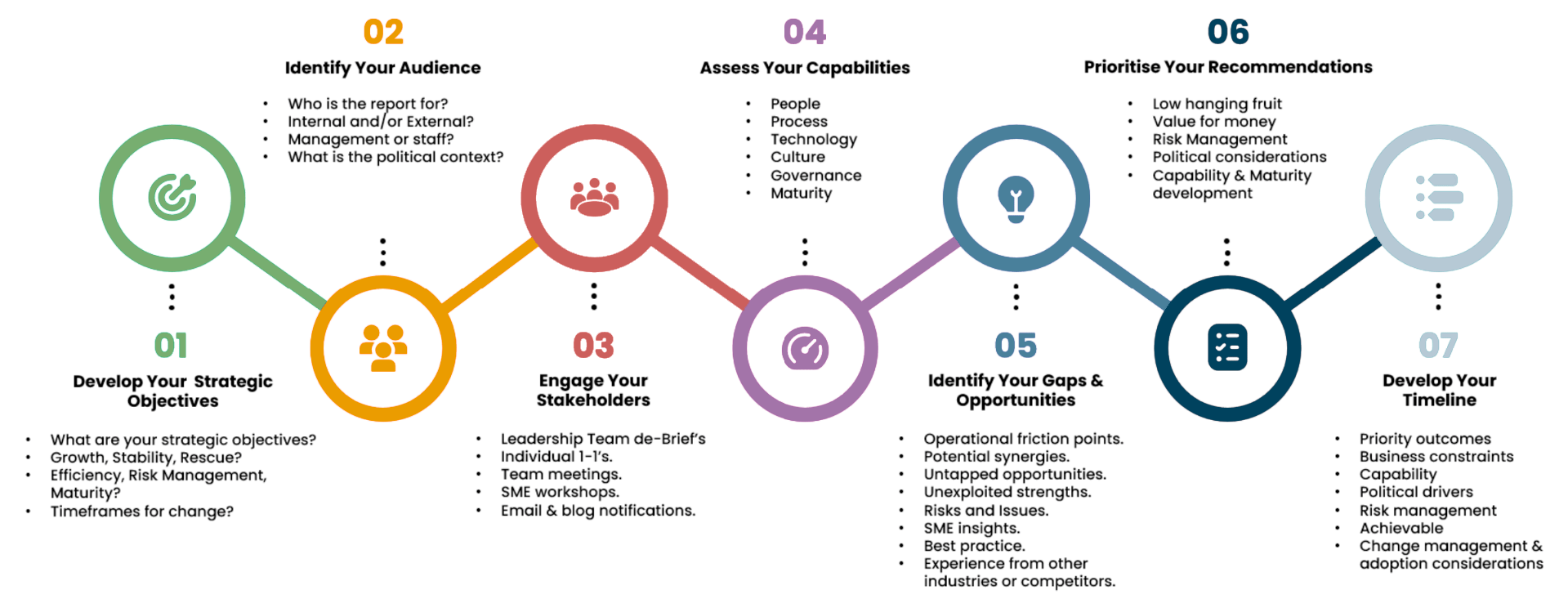
Phases of the Project Roadmap include:

Developing strategic goals:
- In the first stage, teams must clearly define the project's goals—such as stability, growth, or crisis management. These goals establish the roadmap's foundation and direct the team's efforts toward long-term tasks.

Identifying the audience:
- Teams must identify the intended audience for the Project Roadmap. This audience can include external or internal project participants, management, or staff, as well as the political context of their involvement.

Engaging stakeholders:
- Teams engage stakeholders through debriefs, individual meetings, workshops, and email notifications. All participants need a shared understanding of the project's key goals and tasks.

Assessing team capabilities:
- Teams analyze their current capabilities and available resources, including people, processes, technology, and culture. This analysis helps them identify bottlenecks and prepare for task distribution.
Engaging stakeholder Identifying gaps and opportunities:
- Teams evaluate potential synergies, risks, and untapped opportunities. They also determine where the project could face operational challenges.
Prioritizing recommendations:
- Teams must determine priorities, including 'low-hanging fruit' (easily achievable goals), cost-effectiveness, risks, and political factors. This stage structures tasks based on their importance and difficulty.

Developing the timeline:
- During the final stage, teams create the project’s timeline, factoring in business constraints, political considerations, risk management, and team readiness. They ensure that the goals remain realistic and achievable.
Using Tools and Methodologies in the Roadmap #
Jira Product Discovery enhances Project Roadmap development by providing essential tools for managing ideas, prioritizing tasks, and strategic planning. With Jira Product Discovery, teams can:
- Manage ideas at all levels: All team ideas can be recorded, ranked by importance, and then integrated into the roadmap. This provides flexibility and transparency in decision-making processes.
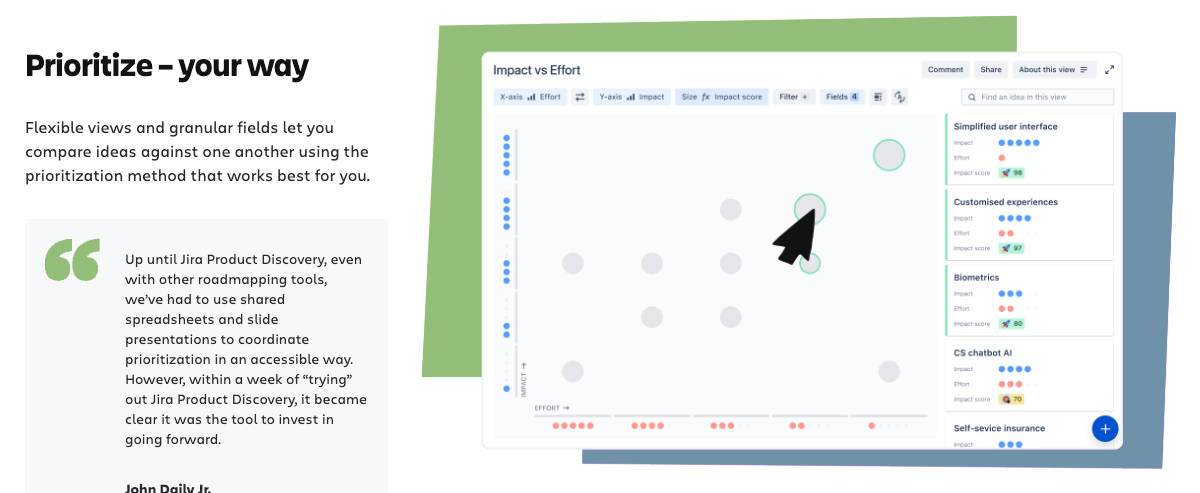
- Prioritize and conduct team voting: With Jira, team voting can be organized, and the impact of each idea on the project and product can be analyzed. The effort required to complete a task can also be factored in. Recent Jira updates allow for more detailed task management by adding customized metrics for priority evaluation.
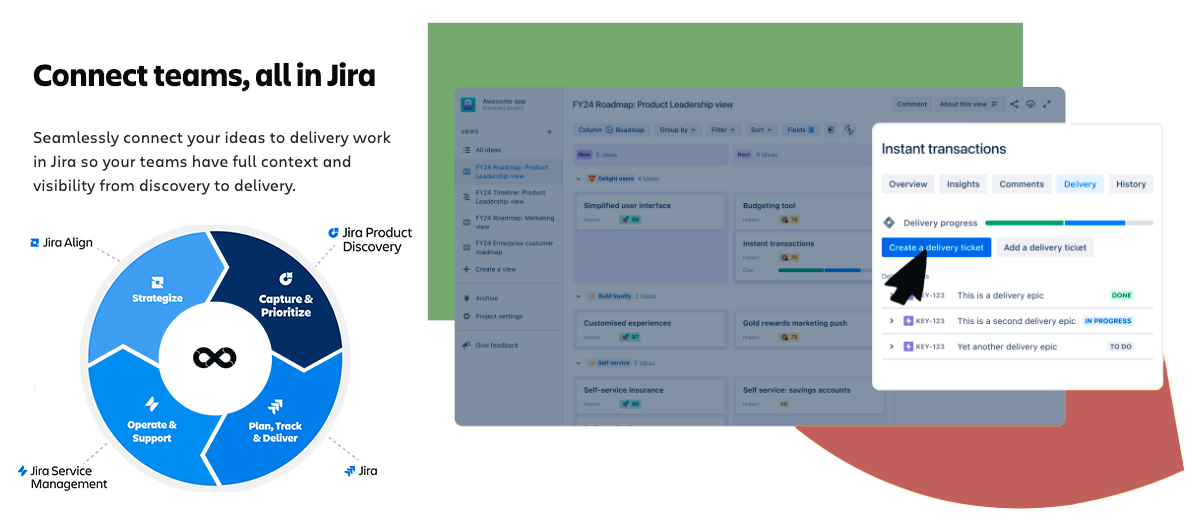
- Integration with other tools: Jira Product Discovery supports integration with various project and task management tools, making it easy to synchronize work between different systems and teams.
A key element here is the integration of templates and methodologies used to structure the project. For example, Agile and Scrum can be applied for more flexible roadmap management, while mind mapping tools can help visualize key stages and features of both the product and the project.
Creating a Draft and Final Roadmap #
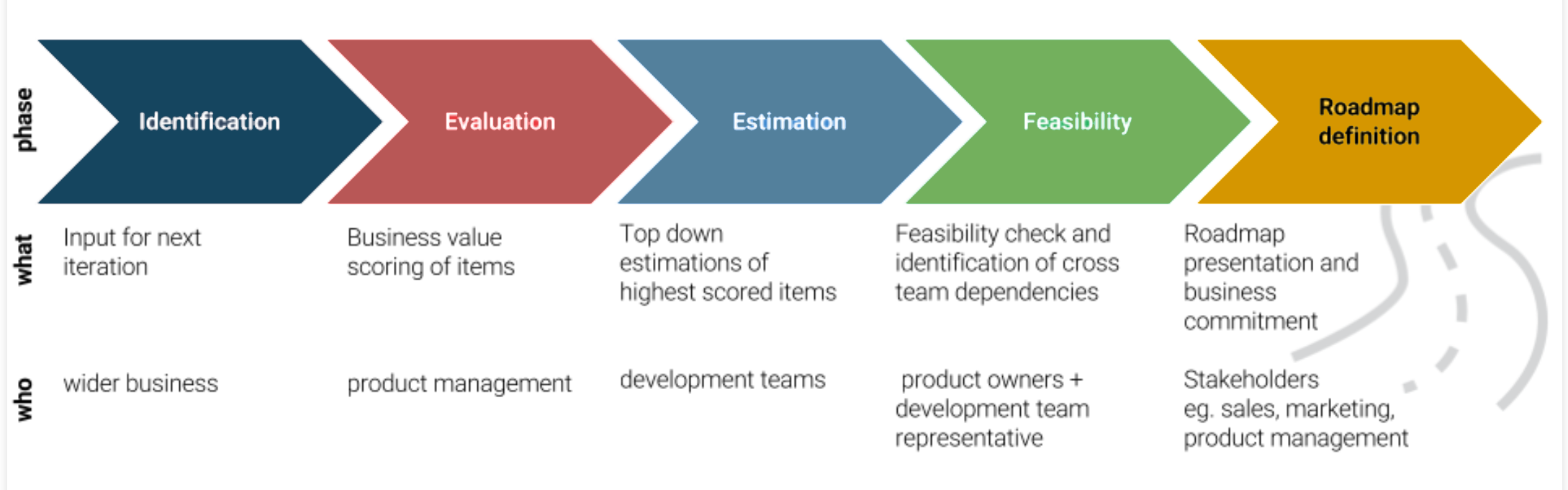
Jira Product Discovery significantly enhances the possibilities of project and product management, providing powerful tools for working with ideas, task prioritization, and strategic planning. Within the Project Roadmap , Jira Product Discovery allows you to:
-
Identification:
At this stage, information for the next iteration is collected. This may include new ideas, updated priorities, and identified opportunities. Broader business groups participate by providing input.
-
Evaluation:
The product team evaluates each idea based on its business impact and ranks them accordingly. This prioritization clarifies which ideas should be implemented first to enhance project efficiency.
-
Effort and time estimation:
Development teams generate high-level estimates for the most critical tasks. These estimations define the implementation order and expected completion time.
-
Feasibility check:
Product owners and team representatives actively conduct a feasibility check. They identify dependencies between teams and tasks, mitigating risks that may affect the project timeline.
-
Final Roadmap definition:
Once all stages are complete, the team prepares the Project Roadmap for stakeholder approval. Marketing, sales, and product management teams provide input to refine the roadmap before finalization.
This is the second roadmap phase, and the second image effectively illustrates how each stage of project development flows from gathering information and evaluation to final approval and presentation of the roadmap.miro.com
Conclusion #
The Project Roadmap should be developed only after completing the Product Roadmap. Since project tasks align with product goals, automation tools like Jira Product Discovery streamline idea management and task structuring. Consequently, development becomes more flexible and transparent.