Topic Definitions #
ERP System
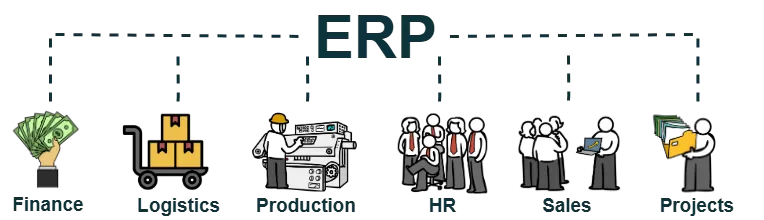
- Finance (budgeting, accounting, reporting);
- Inventory and Logistics (stock management, procurement, supply chain);
- IProduction (planning, monitoring, control);
- IHuman Resources (HR operations, payroll);
- Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM);
- Project and Document Management.
ERP systems help streamline operations, eliminate data duplication, and ensure consistent information flow across departments.
Monolithic Architecture
In a monolithic architecture, all parts of the application are tightly coupled and run as a single process. This means that any change or update to one part of the system requires rebuilding and redeploying the entire application.
Microservices-Based Architecture

Each microservice has its own database, logic, and runtime environment, which allows it to be deployed, scaled, updated, and maintained independently of the others. This provides high flexibility, autonomy for development teams, and simplifies the scaling of the entire system.
Cloud-Native Architecture
EPIC
Work Package
Technology Stack
KPI

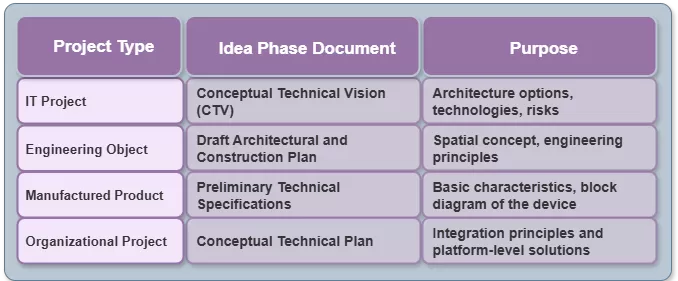
What Is a Technical Product Vision? #
Technical Product Vision is a structured technical overview that describes how a product concept will be implemented within a specific project. It translates previously gathered functional and non-functional requirements, along with the business strategy, into a concrete technical solution. This vision plays a critical role in connecting strategy and execution.
Where Is Technical Product Vision Used?
The Technical Product Vision is applicable across various types of projects, including:
-
Software products
(web services, mobile apps, platforms);
-
Engineering and construction projects
(buildings, infrastructure, structures);
-
Physical products
(equipment, devices, manufacturing lines);
-
Organizational transformations
(ERP implementation, digital transformation).
Each domain uses the vision as a foundation for future design and development efforts.
At the conceptual phase (idea stage), the Technical Product Vision is not a detailed project plan, but rather a preliminary technical direction — outlining possible implementation principles, acceptable technologies, key constraints, and general guidelines.
A strong technical product vision should:
- Align with the company’s overall business strategy;
- Guide technical teams in architectural decisions;
- Ensure scalability, security, and maintainability;
- Encourage innovation and adaptability;
- Provide a clear path for future growth.
Objectives of the Technical Product Vision #
Define the Preliminary Solution Architecture
- For software: A high-level view of the architecture — monolithic, microservices-based, cloud-native, etc.
- For engineering projects: A block diagram of functional zones and draft spatial planning concepts.
- For physical products: A conceptual layout of key components and interfaces.

Identify the Potential Technology Platform
- For IT: Proposed programming languages, frameworks, and environments (with possible alternatives).
- For construction: Preliminary selection of technologies and materials (e.g., frame-based or monolithic structures).
- For equipment: Manufacturing processes, components, and production approaches.

Align the Interaction of Key Components
- At the conceptual level, this includes compatibility principles, data exchange scenarios, and external system requirements.

Define Principles for Scalability, Security, and Quality
- This includes early-stage requirements and benchmarks, such as availability, data protection, and maintainability.
Establish a Foundation for Project Decomposition
- Not in the form of a detailed backlog, but as high-level functional units (e.g., EPICs or Work Packages) that relate to future project phases.
Steps for developing a technical vision for an IT product #

Step 1: Understand Business Objectives and Market Needs
- Before defining the technical vision, it is essential to understand business goals and market conditions. Conduct research to identify:
Customer pain points and expectations
Competitor technology strategies
Industry trends and innovations
Step 2: Collaborate with Key Stakeholders
- Effective technical vision development requires input from:
Product Managers – to ensure alignment with business goals
Engineering Teams – to assess feasibility and implementation
UX/UI Designers – to integrate user experience considerations
Executives & Investors – to secure strategic support

Step 3: Define Technical Principles and Architecture
- Establish core technical principles that will guide development, such as:
- API-first development
- Microservices vs. monolithic architecture
- Cloud vs. on-premises deployment
- Data security and encryption standards

Step 4: Choose the Right Technology Stack
- Select technologies based on:
- Scalability and performance
- Team expertise and availability
- Long-term maintainability
- Cost efficiency
Step 5: Develop a Roadmap with Milestones
- Break down the technical vision into:
- Short-term goals (next 3-6 months)
- Mid-term goals (6-12 months)
- Long-term objectives (beyond 12 months)
Step 6: Ensure Continuous Review and Adaptation
- Technology evolves rapidly, so a technical product vision should be:
- Reviewed regularly (quarterly or bi-annually)
- Adjusted based on market trends, customer feedback, and new technological advancements
A well-crafted technical product vision serves as a guiding force for product development, ensuring that engineering efforts align with business objectives and market needs. By incorporating scalability, security, innovation, and adaptability into the vision, companies can build successful, future-proof products. Developing a strong technical vision is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires collaboration, regular reviews, and continuous improvements.
Components of the Technical Product Vision #
-

Product Vision
This is not the final architecture, but rather a set of possible implementation options and their analysis. For example: a cloud-based platform vs. on-premise.
-
Preliminary Technological Approach
A list of acceptable solutions based on project goals, timelines, and available resources. Possible technologies and standards are considered, but not yet finalized.
-

Integration and Interface Options
Define future integration zones and key constraints for system interaction.
-

General Principles for Quality, Security, and Scalability
Outline approaches for validation, system resilience, and adaptability in later development stages.
Key Components of a Clear Technical Vision for an IT Product
-
Product Goals and Business Alignment
Define what the product aims to achieve and how it supports the company’s mission. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) that will measure success.
-
Technology Stack and Architecture
Choose the right technologies, frameworks, and tools. Define the system architecture, considering scalability, security, and integration needs.
-
User Experience and Performance
Ensure the technical vision supports a seamless user experience. Optimize system performance and reliability.
-
Scalability and Maintainability Options
Plan for future growth with modular and scalable architectures. Implement best practices for maintainable code and efficient deployment processes.
-

Security and Compliance
Address data protection, authentication, and security measures. Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
-
Innovation and Adaptability
Encourage the adoption of emerging technologies. Plan for future enhancements and iterations.
Technical Vision Documentation (at the Idea Phase) #
At the conceptual stage of a project (before design and implementation), only one preliminary document is prepared, depending on the project type:
Possible Components:
Flowcharts and interaction diagrams
Tables of assumptions and constraints
Option and risk maps
Sketch components and architectural layers
Alignment and Responsibility #
At the conceptual phase, the following participants are typically involved:

System architects or technical analysts

Lead engineers or tech leads

Business analysts

Representatives of the customer / project initiator
Conclusion #
The Technical Product Vision serves as a strategic link between business objectives and technical implementation. It defines the conceptual direction for how a product will be designed, developed, and scaled, ensuring that every technical decision supports the organization’s overall goals and market strategy.
By translating functional and non-functional requirements into a coherent technical framework, the vision aligns architecture, technology stack, and quality principles under one unified approach. It provides clarity for teams, enabling effective collaboration, informed decision-making, and consistency across all stages of development.
A well-crafted technical vision is dynamic rather than static — it evolves alongside business priorities, emerging technologies, and user needs. Through regular review and adaptation, it ensures that the product remains scalable, secure, and relevant, guiding the team from concept to long-term success.